At WiseGEEK, we're committed to delivering accurate, trustworthy information. Our expert-authored content is rigorously fact-checked and sourced from credible authorities. Discover how we uphold the highest standards in providing you with reliable knowledge.
What is the Acromion?
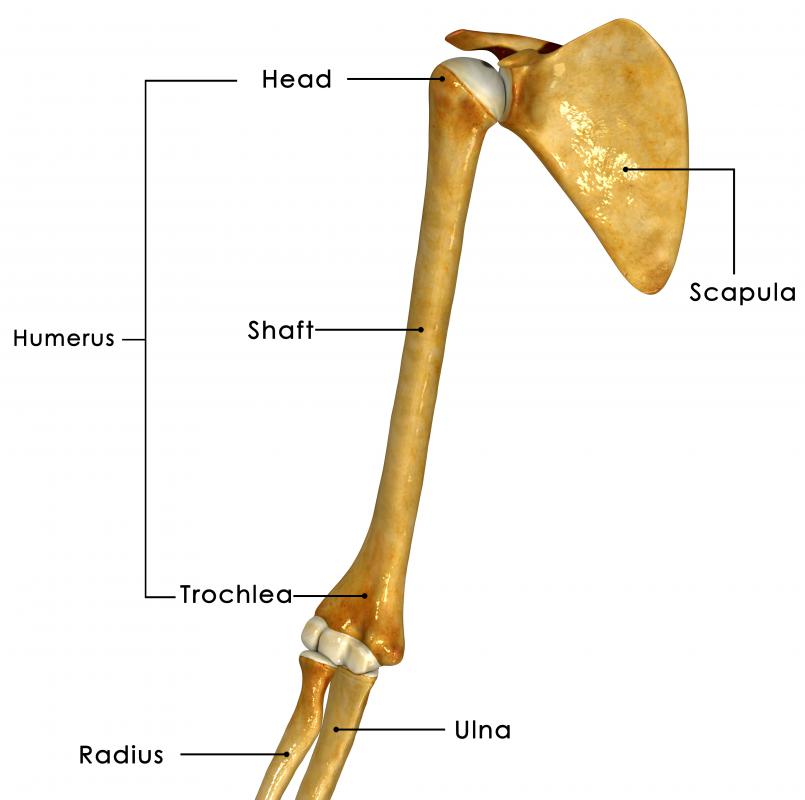
The acromion, also known as the acromion process, is a bony structure on the top of the scapula, or shoulder blade. It arises from a ridge that horizontally crosses the upper portion of the scapula on the back side and protrudes at the peak of the shoulder, forming a club-like shape. Paired with the coracoid process, a similar club-shaped protrusion that arises from the front side of the shoulder blade and crosses laterally toward the shoulder joint, the acromion serves as a point of attachment for the deltoid and trapezius muscles. Its upper surface is convex and rough, angling upward and outward above the shoulder joint, while its lower surface is concave and smooth.
One function of the acromion is to join with the clavicle to form the acromioclavicular (AC) joint. Here the clavicle with its flattened lateral end meets the medial or inside border of the acromion process to form a type of synovial joint known as a gliding joint. In a gliding joint, the adjoining bony surfaces glide past one another. As the articulating surfaces of the clavicle and acromion slide against each other, they make possible the action of raising the arm above the head.

Another purpose of the acromion is to act as a site of muscle attachment. At the shoulder, the fibers of the middle deltoid originate on the lateral border of the acromion process, crossing the shoulder joint and inserting into the deltoid tuberosity partway down the outside of the humerus bone of the upper arm. The main function of the deltoid muscle, particularly its middle fibers, is to abduct the arm, or lift it laterally away from the body. This action occurs at the glenohumeral, or shoulder, joint, but the attachment of the muscle to the acromion provides the leverage that helps to lift the weight of the arm.

The trapezius muscle of the upper back, particularly its middle fibers, also attaches to the acromion. Originating on the spinous processes of the thoracic vertebrae, the middle trapezius crosses the upper back horizontally and inserts into the medial margin of the acromion process. The function of the middle fibers of the trapezius is to retract the scapulae, pulling them back and together. This in turn pulls the arms backward at the shoulder joint, a movement that begins between the shoulder blades and ends with the posterior movement of the shoulders.
AS FEATURED ON:
AS FEATURED ON:












Discuss this Article
Post your comments