At TheHealthBoard, we're committed to delivering accurate, trustworthy information. Our expert-authored content is rigorously fact-checked and sourced from credible authorities. Discover how we uphold the highest standards in providing you with reliable knowledge.
What is Tumor Classification?
A tumor is an abnormal tissue growth which has no physiological function. Tumors are caused by rapid, uncontrolled cell division which continues to expand without treatment. Tumor classification is a system devised by the scientific and medical community to enable practitioners to identify, diagnose and treat tumors.
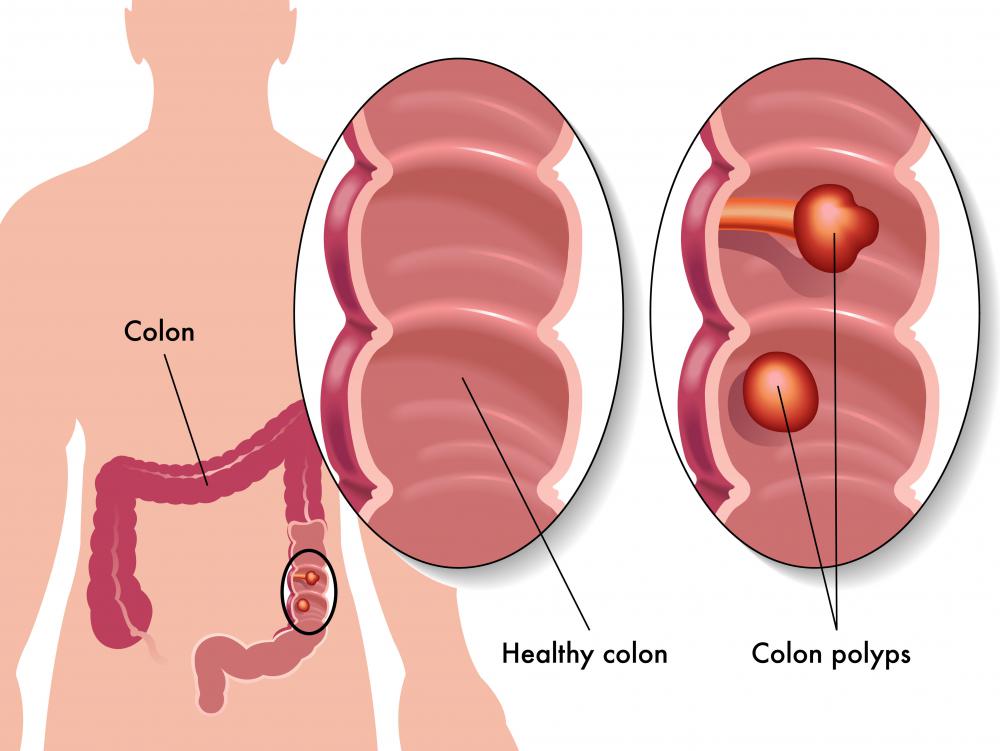
When a tumor is discovered the first step in tumor classification is to determine if the growth is benign or malignant. Benign tumors are slow growing, non-cancerous, and localized, which means that they have not invaded other tissues. These growths can usually be removed and will not come back. Benign tumors can cause serious issues, depending upon their size and location and some, such as polyps in the colon, can become cancerous if not removed.

In contrast, malignant tumors are cancerous and have the ability to spread, or metastasize, into nearby tissues and organs. Cancer cells can also break away from the tumors and get into the blood or lymphatic systems, spreading the disease to other locations in the body. Malignant tumors require swift and specific treatments, so they are the primary focus of tumor classification.

There is no one clear-cut system of tumor classification. At one time, tumors were classified according to how they appeared under a microscope; other systems evolved based upon where the growth originated and the type of tissue it most resembled. As scientific advances have allowed physicians to observe the different cellular and molecular properties of various tumors, new tumor classification systems have emerged. As a result of these changes a single type of tumor may have multiple names, while two different tumors may have the same name. If a patient is diagnosed with a tumor it is important that he not only know the name given to it by the pathologist, but also what staging, or naming system is being used.

The second part of tumor classification is a grading scale which describes the aggressiveness and malignancy of the tumor. Most grading scales range from I to IV, with Grade I describing a tumor which is slow growing and composed of fairly normal cells. Grade II is sill slow growing, with slightly abnormal cells and may recur after removal. Grade III is more serious and applies to more active malignant tumors which are invading nearby tissues. Grade IV tumors are the most critical and are made of fast growing, highly invasive malignant cells.

The tumor classification system employed also varies between the different types of cancers. For example, brain tumors are now generally classified according to the system recently devised by the World Health Organization (WHO). This system classifies the tumor by the type of cells present where the tumor originated and the biological behavior of those cells.

Tumor classification for ovarian tumors depends upon whether they are benign or malignant and the type of cell in which the tumor originated. Tumors which start in the surface of the ovary are called epithelial tumors. Those which start in the cells that produce the eggs are called germ cell tumors, and tumors which start in the cells which produce hormones are called stromal tumors.
AS FEATURED ON:
AS FEATURED ON:














Discuss this Article
Post your comments