At WiseGEEK, we're committed to delivering accurate, trustworthy information. Our expert-authored content is rigorously fact-checked and sourced from credible authorities. Discover how we uphold the highest standards in providing you with reliable knowledge.
What is the Auditory Nerve?
The auditory nerve helps to send sound signals or vibrations to the brain. It sits behind the cochlea and connects to the vestibular organ or semi-circular canals. This nerve is a part of the inner ear and it is just one of the many parts of the ear that allow us to hear sounds. They all work together to send these sounds or vibrations to the brain for processing. The auditory nerve contains receptor neurons.
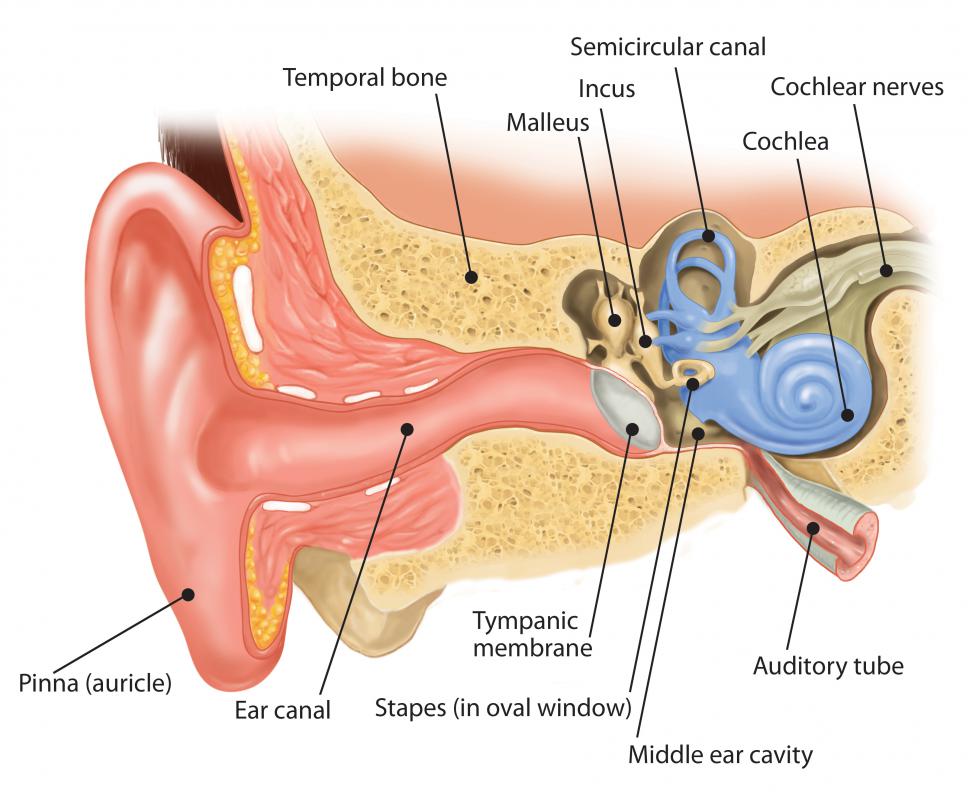
To fully understand how the auditory nerve works, it is important to know how sound is heard. When people hear sounds, they are really experiencing vibrations or waves of sound. These vibrations enter the ear through the pinna. This opening connects to the ear canal and it is shaped like a megaphone. It enhances vibrations and makes them easier to sense.

The eardrum sits in the ear canal and it is there to protect the middle and inner ear because it acts like a shield. There are three tiny bones that are located behind the eardrum. When a vibration hits the eardrum, these bones vibrate. They are refereed to as the stirrup, anvil, and hammer and they all vibrate one after the other, until the sound is passed on to the inner ear.

Sound enters the inner ear by way of the cochlea. This is a fluid-filled sac that also vibrates when sound is heard. The basal membrane within the cochlea then passes the vibration to the auditory nerve by way of the organ of corti. This organ is actually cells that are referred to as hair. These hairs connect directly to the auditory nerve.
This process not only allows us to hear but also sense other things. Pitch and loudness can also be determined by vibrations within the ear. For example, the organ of corti already amplifies sound but if the noise is extremely loud, it causes the cells or hair to vibrate more intensely. It then sends the information through the auditory nerve and the brain perceives it as a loud noise.

Damage to the auditory nerve can result in permanent hearing loss. This is called neural hearing loss and it can be caused by certain diseases or medical conditions. Hearing loss caused by illness can be avoided by early detection. Hearing can be partially or fully restored if the auditory nerve is not damaged severely.
AS FEATURED ON:
AS FEATURED ON:
















Discuss this Article
Post your comments