At WiseGEEK, we're committed to delivering accurate, trustworthy information. Our expert-authored content is rigorously fact-checked and sourced from credible authorities. Discover how we uphold the highest standards in providing you with reliable knowledge.
What is the A1C Test for Diabetes?
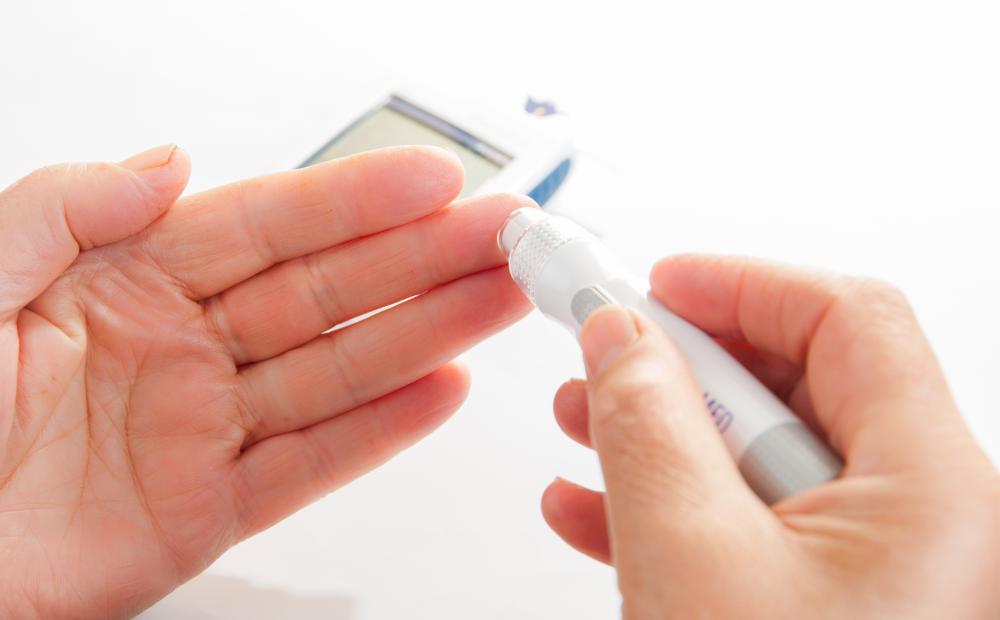
The A1C test measures a diabetic person's blood sugar levels for the previous three months to give an overall view of how under control glucose levels are. The test is also referred to as the HbA1C and it differs from daily glucose monitoring that diabetics do themselves as daily glucose testing is designed to check what the blood sugar level is only for that moment of testing. By using the A1C test to measure a patient's blood sugar averages for the past few months, a doctor can get a better idea of how well diabetes treatments are working to help lower glucose in the blood.
Diabetics must keep blood glucose levels under control to prevent the risk of complications of diabetes such as damage to blood vessels, nerves, eyes and kidneys. Daily monitoring of blood sugar levels is crucial for diabetics, but so is the A1C test. The A1C test is designed to average blood sugars over a period of a few months as that is how long a red blood cell lives in the body. The way that the A1C test works to average blood sugars over the span of a few months is to measure the percentage of glycated hemoglobin, or A1C, or excess sugar that connects with the hemoglobin inside red blood cells. The higher the diabetic's amount of excess glucose, the higher the percentage of A1C present in the body.

Old blood cells are replaced by new blood cells in the body after 120 days, so the A1C is designed to measure glucose levels every three months. Many medical professionals recommend that diabetics get an A1C test a minimum of twice a year — more if the results of a previous test show poor control. The high end of the A1C test is considered to be a blood glucose measurement of 25%, while 5% is considered a normal blood glucose level. Non-diabetics given the A1C test should test at about 5%. The percentage is the measurement of glycated hemoglobin in the body.

A percentage under 7% is considered good blood glucose control for most diabetics. However, the goal is usually 6% for pregnant women and ideally that number should be reached before a diabetic woman conceives. Keeping blood sugar levels at a consistently lower level can help reduce or avoid complications from diabetes that include kidney disease, eye disease and nerve damage.
AS FEATURED ON:
AS FEATURED ON:














Discussion Comments
@burcidi-- I tried an A1C home test and I think the accuracy is pretty good but I still wouldn't replace the laboratory A1C test with it altogether.
The same month I tried the home kit, I also got the laboratory test which was a good chance to see if they would give similar results and they did. My laboratory test came back 5.8% and my home test showed 6.0% which is pretty close.
The reason I won't stop the laboratory test however is because the A1C test at the hospital uses blood drawn from the arm. Whereas the home kit uses the prick pen. I've heard that results from the prick pen and the laboratory blood draw can never be the same.
The hemoglobin A1C test can also be used for diagnosis right? What are the disadvantages and advantages of diagnosing using the A1C test rather than a glucose tolerance test? I was diagnosed with the glucose tolerance test but I'm just curious.
Also, I've heard that there are now A1C home kits available on the market. Has anyone tried one of these? What do you think about the accuracy?
I personally hate having to see my doctor for this test every three months because it's a long drive and they always make me wait forever for the results. It would be great if I could do it on my own at home. But I wonder if it would as dependable as a laboratory test?
My mom goes for the A1C blood test every three months. She tells me that it's even more important than her daily readings because it will let her know how she's been doing the past couple of months.
If she has followed her diet carefully, took her medications on time and exercised, the results of the A1C test always come back good. She's so happy when they do.
But if she ate too many of the foods she's not supposed to or skipped her medication at any time, the A1C shows that. The results come back too high and it's a warning for my mom to get back on track.
I'm glad that the A1C blood test is available. It's like a control mechanism for diabetics. Otherwise diabetics might ignore their treatments and diet.
Post your comments