At WiseGEEK, we're committed to delivering accurate, trustworthy information. Our expert-authored content is rigorously fact-checked and sourced from credible authorities. Discover how we uphold the highest standards in providing you with reliable knowledge.
What is a Mantoux Test?
A Mantoux test is a skin test used to test someone for signs of exposure to Mycobacterium tuberculosis, the bacterium that causes tuberculosis infection. This type of test may be ordered in a wide variety of circumstances, from a routine physical to a medical examination performed as part of the requirements for a job. Because tuberculosis is highly infectious, people who seek employment in schools and government agencies are often asked to get tested as a term of employment.
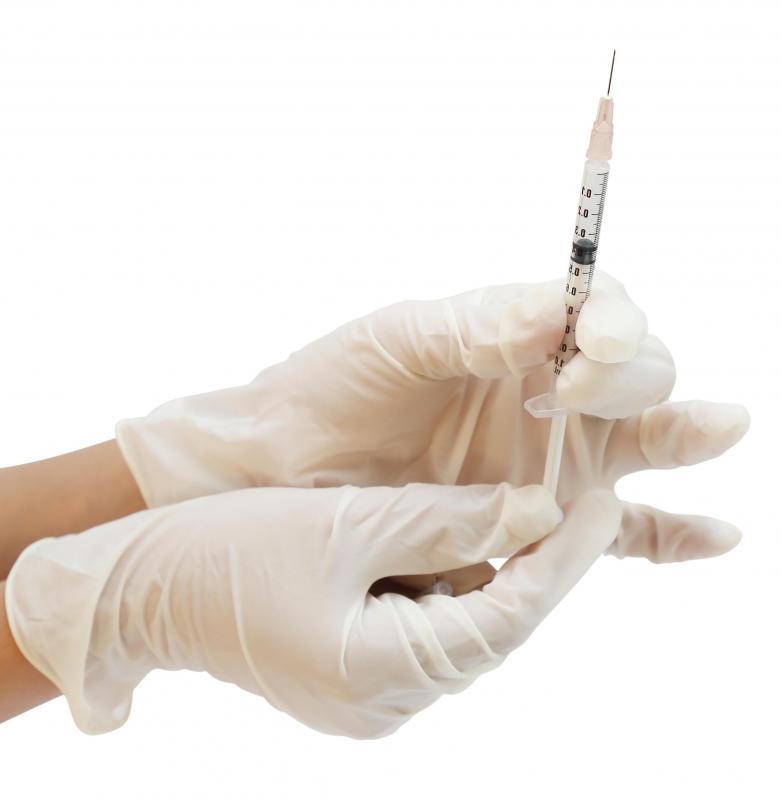
In this test, a medical professional injects a small amount of protein from the tuberculosis bacterium under the skin of the arm. This substance is known as tuberculin or purified protein derivative (PPD). It cannot cause tuberculosis, but it will spur the immune system to react, causing an area of raised skin to appear at the injection site if someone has been exposed to or infected with tuberculosis.

After the injection, the patient is sent home for two to three days. He or she must return to a medical professional's office to have the test read. In a negative test, little to no swelling has occurred. Positive tests cause the appearance of a raised disc, which can be between about 0.2 and 0.6 inches (5 and 15 millimeters) in diameter. If someone has a compromised immune system, the smaller reading is considered positive. In individuals with risk factors for tuberculosis exposure, the raised skin should measure at least 0.4 inches (10 mm) for a positive reading, while individuals who are at low risk would have positive readings if the area was 0.6 inches (15 mm) or more in diameter.

It is possible to get a false negative on a Mantoux test, in the case of someone who was exposed lightly, or infected and treated more than 15 years prior to the test. People who have been infected and treated may experience false positives, in which the test makes it look like the patient is actively infected, but he or she cannot pass the bacterium on to others because it is not present. In these cases, additional diagnostic tests can be used to confirm that the patient is free of the bacterium.

If a Mantoux test is positive, the patient will be advised to seek medical advice from a healthcare professional who can perform additional diagnostic tests and offer treatment recommendations. Generally, these tests will include X-rays to check on lung function. If the patient does indeed have an active tuberculosis infection, antibiotic medications can be provided to kill the bacteria in the body. A person with a positive test may be barred from employment in certain types of jobs until he or she can provide documentation indicating freedom from tuberculosis.
AS FEATURED ON:
AS FEATURED ON:














Discussion Comments
when getting a 2 step mantoux PPD skin test, how many days from the first shot to the second one? I was told 7-10 but then also told 7-21.
To answer lokilove as I understand it: if exposed to TB there is a chance you have latent TB (not infectious). When it becomes active, you have TB disease (infectious and a notifiable disease).
When exposed to a person with active TB, your immune system says "That's not supposed to be there" (Really, it says that) and it walls it off to protect you.
In doing so, you form antibodies. When you are given a Mantoux test the small Tuberculin protein causes the body to recognize it and react.
The problem with having "latent" vs. active tb is that it is hanging out in your lungs and may become active tb if your immune system isn't strong enough to hold it isolated.
This usually happens in the first two years after infection. Ten percent of those with latent TB will develop active TB at some point in the future.
A medication can be taken (INH) for nine months to prevent that later reactivation.
I don't understand why the immune system reacts to the test if the tuberculin isn't active. Also, if you don't HAVE tuberculosis why does having ever been exposed to it, important?
Post your comments