At AllThingsNature, we're committed to delivering accurate, trustworthy information. Our expert-authored content is rigorously fact-checked and sourced from credible authorities. Discover how we uphold the highest standards in providing you with reliable knowledge.
What Are Bone Marrow Macrophages?
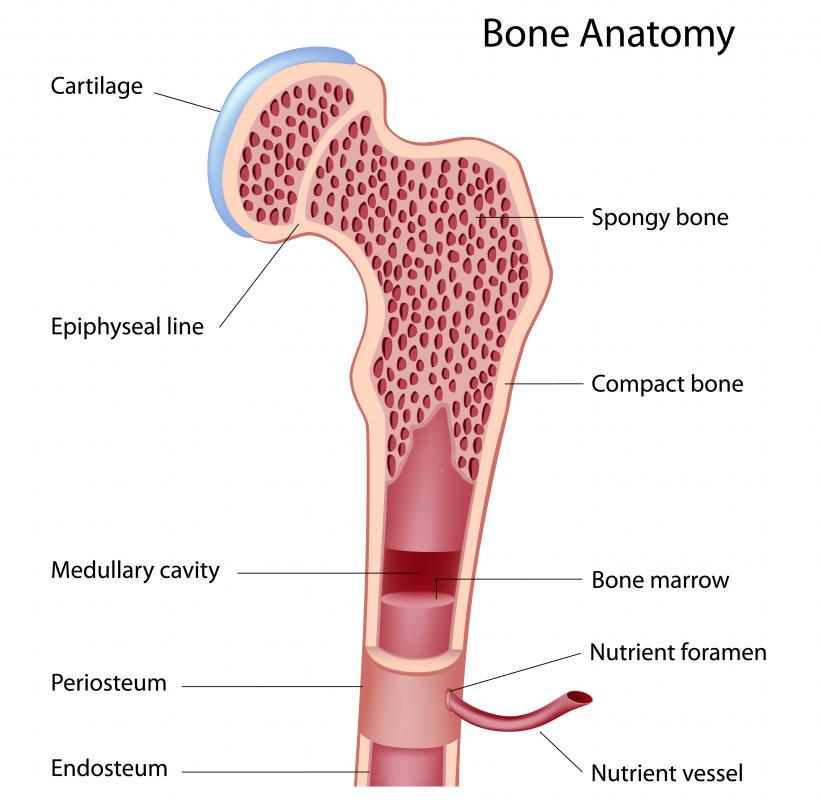
Bone marrow macrophages are a type of white blood cell, or leukocyte, that attack and digest invading bacteria, tumor cells, protozoa, which are single-celled organisms, and other hostile germs that can invade and infect a living host organism. They are part of the immune system and have the ability to stimulate the activity of other types of immune cells. As their name suggests, bone marrow macrophages are created in the marrow, or the inner tissue, of the bones of animals and humans. The term bone marrow macrophages can refer to either naturally produced cells, or cells created in an in vitro environment, meaning that they're produced in a laboratory setting rather than made naturally in the body of a living animal. The term bone marrow-derived macrophages refers specifically to macrophage cells that are created in vitro.
Macrophages can be created in a laboratory by artificially growing mammalian bone marrow. This is achieved by exposing undifferentiated cells, or immature cells without a defined structure, to the macrophage colony-stimulating factor (M-CSF), which is a type of growth factor, or more simply, a hormone that controls the growth and maturation of macrophage cells. These new bone marrow cultures are grown in Petri plates, which are also known as culture dishes.

Hematopoiesis, which can also be spelled haematopoiesis, is the process by which the body naturally creates all the different types of blood cells, or blood components, including bone marrow macrophages. Hematopoietic stem cells are responsible for the process of hematopoiesis. All multicellular organisms have stem cells. They can divide, reproduce, and turn into a variety of specialized cell types, meaning they can turn into different types of cells that perform different biological functions. They also have the ability to repair damages cells.

All blood cells are divided into three categories, referred to as lineages. Bone marrow macrophages belong to the myelocyte lineage. The process called myelopoiesis refers to both the production of cells that belong to the myelocyte lineage, and also to the process that creates bone marrow tissue.
When marcophages are first created in bone marrow, they are referred to as monocytes. After they migrate to other parts of the body via the bloodstream, they mature into macrophages. These new macrophage cells stay permanently in bodily tissues where they protect against invading germs and tumor cells by both engulfing and dissolving them, and by alerting other immune cells to the presence of invasive cells or organisms.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are bone marrow macrophages and what is their primary function?
Bone marrow macrophages are specialized immune cells originating from the bone marrow. Their primary function is to maintain bone health by removing old, damaged, or dead cells, a process known as phagocytosis. They also play a crucial role in regulating the formation of new blood cells and maintaining the bone marrow environment.
How do bone marrow macrophages contribute to the immune system?
Bone marrow macrophages contribute to the immune system by acting as the first line of defense against pathogens. They identify, engulf, and destroy bacteria, viruses, and other foreign substances. Additionally, they present antigens to T cells, which is essential for initiating an adaptive immune response, according to immunology studies.
Can bone marrow macrophages affect bone density?
Yes, bone marrow macrophages can affect bone density. They interact with osteoclasts, the cells responsible for bone resorption. Through the secretion of various factors, macrophages can influence osteoclast differentiation and activity, thereby impacting bone remodeling and density, as reported in bone health research.
What diseases are associated with bone marrow macrophages?
Diseases associated with bone marrow macrophages include osteoporosis, where an imbalance in their activity can lead to increased bone resorption. They are also implicated in inflammatory conditions like rheumatoid arthritis and can be involved in certain cancers, such as leukemia, where their regulation of the bone marrow environment is disrupted.
Are bone marrow macrophages involved in any medical treatments?
Bone marrow macrophages are involved in medical treatments such as bone marrow transplants. They play a role in graft acceptance and the re-establishment of the recipient's hematopoietic system. Research is also exploring their potential in immunotherapy, given their ability to present antigens and activate T cells.
How are bone marrow macrophages studied in scientific research?
Scientific research on bone marrow macrophages involves various techniques, including flow cytometry to analyze their surface markers, microscopy to observe their interaction with other cells, and molecular biology methods to study their gene expression. Animal models and in vitro cultures are also used to understand their behavior in different conditions.
AS FEATURED ON:
AS FEATURED ON:











Discuss this Article
Post your comments