At WiseGEEK, we're committed to delivering accurate, trustworthy information. Our expert-authored content is rigorously fact-checked and sourced from credible authorities. Discover how we uphold the highest standards in providing you with reliable knowledge.
What Was the Warsaw Pact?
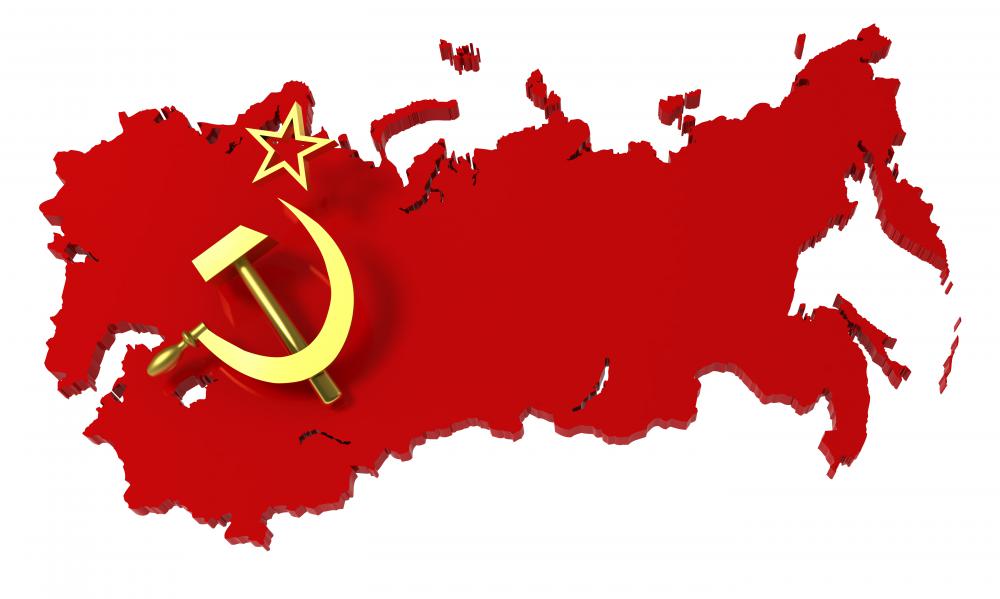
The Warsaw Pact is the name given to an agreement, established in Poland in 1955, between several Communist states of Europe. It is also known as the Warsaw Treaty of Friendship, Cooperation and Mutual Assistance. The Soviet Union initiated the agreement in response to the formation of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO), which in turn was formed in response to the perceived threat to European and North Atlantic nations by the Soviet Union. The Warsaw Pact was made available in Polish, Czech, German, Hungarian, Romanian, and Russian.
Originally, the members of the group that signed the pact included the Soviet Union, Bulgaria, Albania, Hungary, Poland, Romania, and Czechoslovakia. The German Democratic Republic joined in 1956, and Albania left the pact in 1961 after the Sino-Soviet split. The agreement ultimately dissolved in 1991 as the Soviet Union fell apart and many of the Communist states that made up the pact moved to democratic systems.

The Warsaw Pact had two main duties and two main branches. The Political Consultative Committee was responsible for non-military activities between the various nations that made up the pact. The Unified Command of Pact Armed Forces was responsible for the various troops under its auspices from the various nations that made up the pact. The Supreme Commander of the Unified Command was also the First Deputy Minister of Defense for the Soviet Union itself.

The basic idea of the agreement was that the various nations who were signatories would come to one another’s aid in case of outside aggression. There were fears among many of the members that Western nations, especially after the formation of NATO, might choose to invade or take military action against the Eastern Bloc states to try to topple their Communist governments. The Warsaw Pact assuaged these fears somewhat by combining each nation’s military power into a much greater force. The Soviet Union also used the agreement as a way to control its smaller allies, as it did when it swept into Czechoslovakia in 1968 with the assistance of other pact members to overthrow a government it said was showing imperialistic tendencies and, therefore, threatening other pact members.

In spite of the Cold War and the rivalry between NATO nations and nations that were a part of the Warsaw Pact, there were many examples of mutual cooperation between the two. Both groups often deployed troops under the auspices of the United Nations, who would serve side by side with one another. The International Commission of Control and Supervision, for example, deployed both Canadian and Polish troops to Vietnam.

In 2005, Poland released many classified documents from the time of the agreement, which shed light on much of the strategy of the member nations. Most surprising to many were the contingency plans of the nations in the case of a war with the Western powers. The primary strategy was incredibly offensive, with plans laid out on how to deploy quickly and effectively into Western Europe to seize control, using nuclear force if necessary. Very few defensive plans were found, with the strategy relying on speed and efficiency to neutralize European powers.

A number of former Warsaw Pact member nations, and the governments that have since replaced them, joined NATO in 1999. In 2004, even more joined. The membership of Bulgaria, Poland, Hungary, Estonia, Latvia, Romania, Slovakia, the Czech Republic, and Lithuania represents in many ways a closing of one of the last circles of the Cold War.
AS FEATURED ON:
AS FEATURED ON:















Discussion Comments
@hangugeo112
I would not say that was the end of the story. As NATO came to Eastern Europe there were many nations which wanted nothing to do with it, as we saw in the tragic history of hatred and discrimination in the Balkans. There are still so many deep societal scars in those regions that ward off a good economy and may take generations to heal.
Poland and many Slavic nations traded one reign of terror for another when the Soviets drove Hitler back. Hitler and Stalin were arguably two of the worst tyrants of the 20th century, and to have lived in the region over which the Warsaw Pact held influence was a very restrictive existence. At the collapse of the USSR and the breaking of the Berlin wall, a new era had finally been ushered in for Eastern Europe.
Post your comments