At SmartCapitalMind, we're committed to delivering accurate, trustworthy information. Our expert-authored content is rigorously fact-checked and sourced from credible authorities. Discover how we uphold the highest standards in providing you with reliable knowledge.
What Is the Retail Value Chain?
The retail value chain is a series of activities that make it possible for businesses to sell goods to consumers. Each activity provides a small part of value to the overall process. Four steps are common in the retail value chain: manufacturer, warehouse, carrier, and supplier. All parts are necessary for retail stores to stock their shelves with consumer goods. Though each activity adds a small portion of cost to the products flowing into the retail store, the costs are typically less than the retail store going directly to each manufacturer for goods.
Manufacturers are the businesses that produce goods. They are commonly referred to as conversion agents. They take raw materials and labor as inputs, using these items to produce goods valued by customers. Few manufacturers actually have the ability to ship goods directly to retail venues. This requires the need for partners in the retail chain to take goods from the manufacturer to warehouses via carriers.

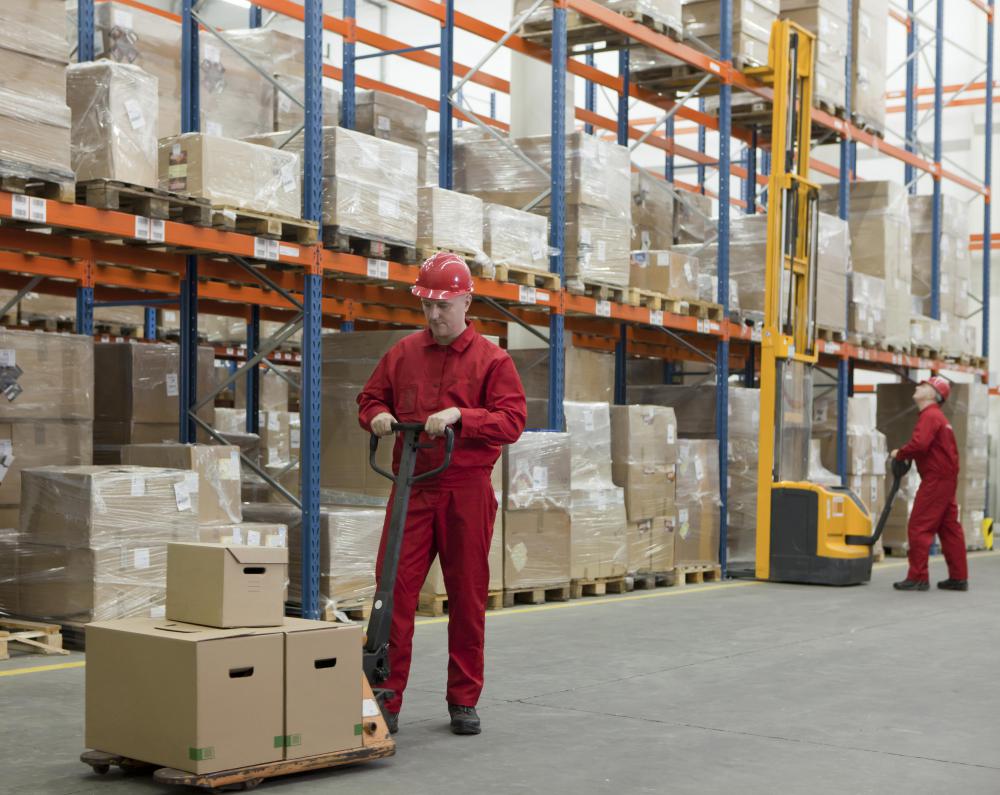
Warehouses store a variety of retail goods in their facilities from several manufacturers. They contract with a number of different producers to stock goods for easy distribution to retail stores. Larger retailers may have their own warehouses. This allows the retailers to locate distribution centers in strategic areas to deliver goods easily to retail stores.

Carriers represent trucking companies that move goods from one point to another. They deliver goods from manufacturers to warehouses and warehouses to retail stores. Their sole purpose in the retail value chain is to work as a service for each company. Retailers rarely have trucking divisions as part of their retail businesses. They contract this service out to save costs on insurance, fuel, wages, and maintenance.

Suppliers are the final step in the retail value chain. Retailers may own their own supply chains as part of their retail companies. These are the localized distribution centers that deliver goods straight to retail stores. Not all retail value chains have suppliers as part of their processes. Retailers can avoid these businesses by working directly with warehouses to deliver goods into their retail outlets.

Technology allows retailers to shorten the ordering process within the retail value chain. Electronic ordering ensures that retail stores order goods in a real-time format. This helps avoid stock outs and reduces the possibility of losing sales from consumers. Electronic systems also remove human flaws from the ordering process. Employees do not need to write paperwork or make phone calls to suppliers, warehouses, or manufacturers.
AS FEATURED ON:
AS FEATURED ON:














Discussion Comments
@PinkLady4 - A cousin of mine worked in the supplier section of a retail value chain. She said the system is really quite complicated and it is changing all the time, partly due to globalization and the added competition.
I guess the main idea is that the parts of the retail chain must constantly share information so that shared goals are met, such as getting the product onto the shelves at the right time.
Each link needs to be able to look at and evaluate what is going on in every other link.
This is some general explanations for your questions. I really don't know how the specifics work. Anyone?
I'm a little confused about this retail supply chain. Are the carrier, and the supplier both under contract with the manufacturer? In the buying process, does that retail dealer order from the supplier?
There could be a variety of disputes between the four parts of this chain. Who deals with and settles problems?
In the first step, who do retailers initially order from when they want merchandise on their shelves?
Can anyone explain?
@sunnySkys - That is something to think about!
I'm more interested in what would happen if electronic ordering broke down for some reason. I know at my job we're so used to doing things with the aid of computers we wouldn't know what to do if the computers went down!
It seems like it's a pretty long process to actually get good onto the shelf at the store! I think a lot of us really take our consumer goods for granted, but imagine if one link on the chain broke?
For example, what if truckers went on strike or something? Then how would the goods get from the warehouse to the store? It's actually a little bit scary to think about.
Post your comments