At TheHealthBoard, we're committed to delivering accurate, trustworthy information. Our expert-authored content is rigorously fact-checked and sourced from credible authorities. Discover how we uphold the highest standards in providing you with reliable knowledge.
What Is the Difference between Coagulants and Anticoagulants?
Both coagulants and anticoagulants are substances that have a primary use in the medical world. They both deal specifically with blood, but the difference lies in the impact each has on this substance. Coagulants promote blood clotting and are therefore mostly used as a means of blood loss prevention. In contrast, anticoagulants hinder the formation of blood clots or dissolve already-formed clots. These substances primarily prevent blood flow blockages.
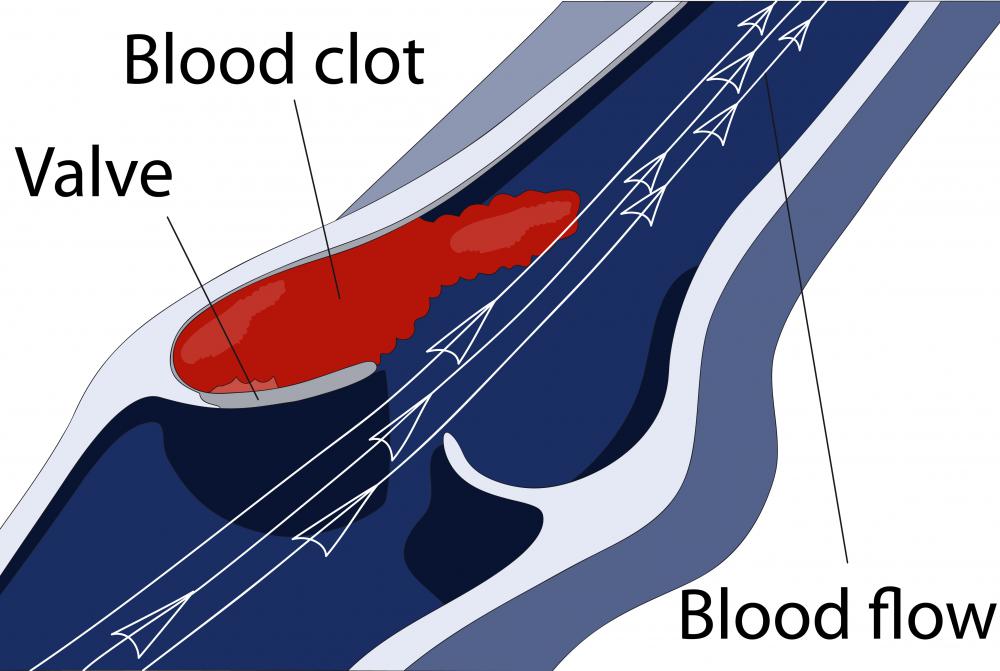
The body uses clotting as a mechanism for alleviating the consequences of blood vessel damage. When trauma tears or otherwise hurts a blood vessel, bleeding occurs. Abundant blood loss can cause a number of dangerous consequences, from body shock to death. In order to stop bleeding, cell fragments called platelets join with particles known as fibrin molecules to thicken the blood around a wounded area. Subsequent coagulation thus stops the flow of blood outside the vessels.
Coagulants are drugs designed to help facilitate the clotting process. Some, such as desmopressin, strengthen platelets. Others, like prothrombin complex concentrate, combat the work of anticoagulant agents.

The hereditary disorder hemophilia perhaps best represents conditions that benefit from coagulants. In this condition, abnormalities hinder the proper formation of blood clots, which leads to prolonged bleeding even with minor cuts and scrapes. Managing this condition often necessitates the use of coagulation substances like Factors VII, VIII, and IX. These protein substances work with a material called tissue factor found outside blood vessels to create clotting agents.

Coagulants and anticoagulants differ in their aims toward clotting. While blood clots are beneficial most of the time, they can cause their own damage in some cases. Irregularities such as unusual blood composition or flow may cause the formation of unwanted and large clots inside blood vessels: a consequence known as thrombosis. These clots can eventually block the regular flow of blood, which may prevent parts of the body from receiving oxygen or other needed nutrients. If the blood clot travels to the lungs or brain, resulting damage from a stroke or pulmonary embolism can be particularly severe.

Scientists have developed anticoagulants as ant-clotting measures for the aforementioned scenarios. Antithrombin-activating heparin and vitamin K-antagonizing coumadin are two substances that may prevent unwanted clotting. Other anticoagulants directly work against clotting rather than activating or inhibiting a natural body substance for the task. These types include hirudin and argatroban. Likewise, plasmin and recombinant human tissue plasminogen activator (TPA) can help dissolve already-formed clots.

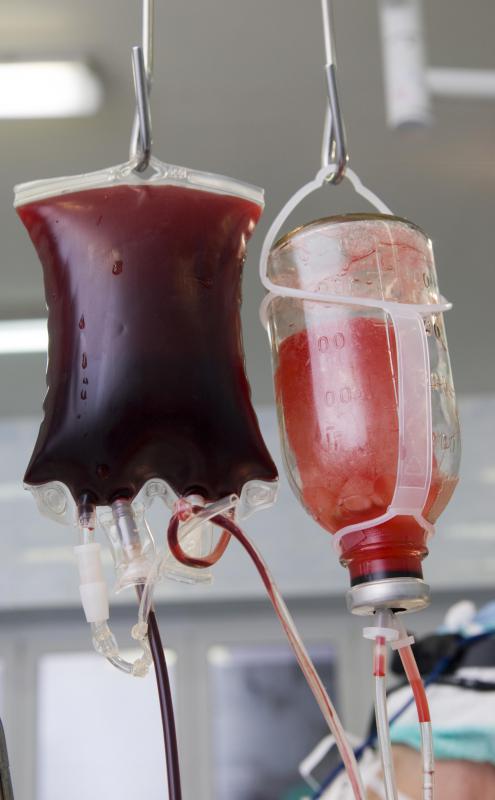
In addition, medical professional often add anticoagulants to equipment that routinely holds or transports blood. Such equipment ranges from transfusion bags to test tubes. Blood should remain in a normalized state for medical procedures, so the anticoagulants help prevent inconvenient thickening. The presence of anticoagulants in medical equipment represents another distinction between coagulants and anticoagulants.

Generally speaking, the uses of coagulants and anticoagulants are at cross-purposes. The substances and processes that anti-coagulants work to hinder, coagulants will seek to promote and preserve. Further, the dangers of coagulants and anticoagulants are strongly divergent. While coagulants run the risk of forming unwanted clots, anti-coagulants run an equal risk of causing excessive bleeding.
AS FEATURED ON:
AS FEATURED ON:
















Discuss this Article
Post your comments