At WiseGEEK, we're committed to delivering accurate, trustworthy information. Our expert-authored content is rigorously fact-checked and sourced from credible authorities. Discover how we uphold the highest standards in providing you with reliable knowledge.
What is the Corpus Spongiosum?
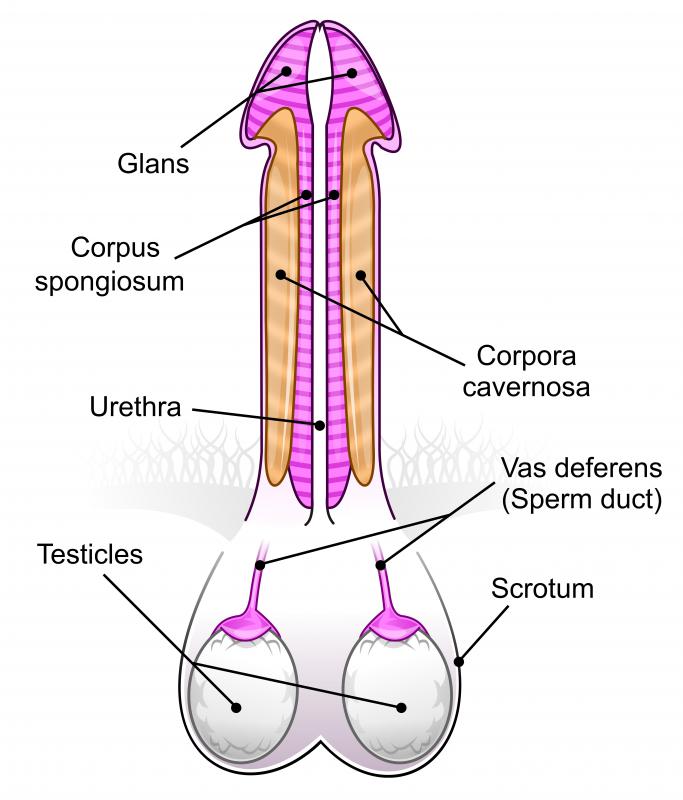
The corpus spongiosum is a spongy tissue in the penis. Sometimes this tissue is also referred to as the corpus cavernosum urethrae, although that term is considered outdated. It surrounds the urethra and prevents it from being compressed and closed when the penis is erect. Without theis tissue, the urethra would pinch shut during erection, making it impossible for semen to pass through the penis during ejaculation.
At its most internal point, the corpus spongiosum forms a bulb, through which the urethra enters the penis. This tissue then tapers somewhat through the length of the penis, finally enlarging again to form the glans, or the head of the penis. Surrounding and supported by the corpus cavernosa, the erectile tissue of the penis, the glans is the most sensitive portion of the penis. During an erection, the corpus cavernosa engorges as blood flows into it. The corpus cavernosa becomes hard and inflexible, but the sponge-like tissue of the corpus spongiosum remains pliable.

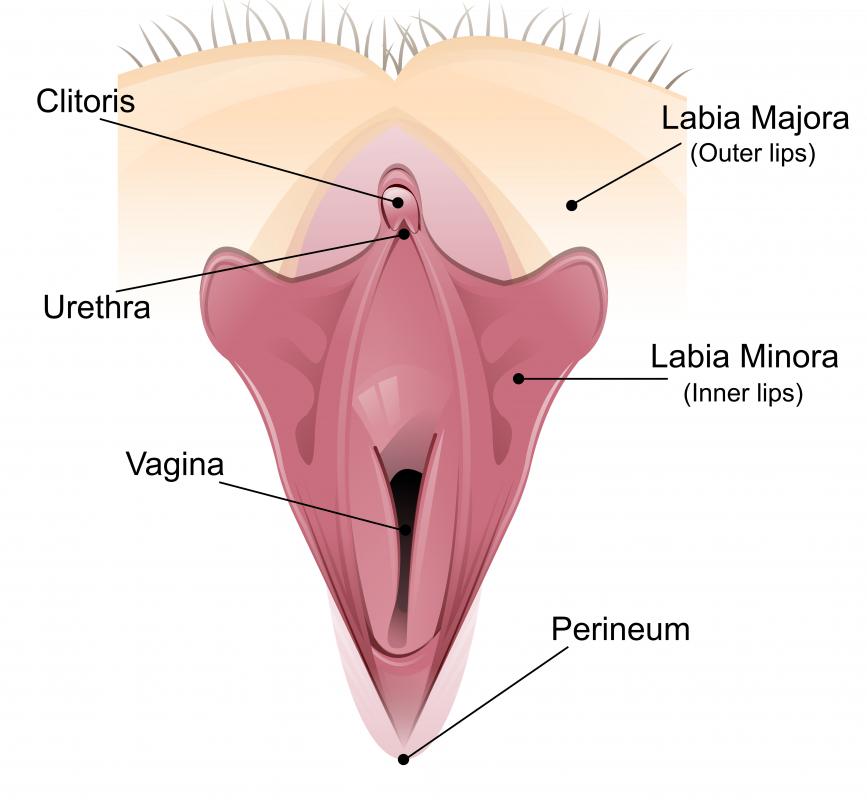
Female sex organs contain tissue similar to the corpus cavernosa. In the female, the erectile tissue, called the corpus cavernosa clitoridis, forms the clitoris, which also becomes engorged with blood and erect during sexual stimulation. Unlike the penis, the clitoris does not contain a corpus spongiosum, because the urethra does not pass through the female erectile organ and thus does not need to be protected when the clitoris becomes erect.

Damage to the corpus spongiosum or to the corpus cavernosa can cause difficulty in achieving an erection or can cause reduced sensation during sexual activity. It can be damaged because of priapism, a condition in which an erection lasts longer than usual and becomes persistent and painful. It can also be damaged as a result of injury to the penis.

In rare cases, the corpus spongiosum is completely missing, resulting in a congenital condition called scaphoid megalourethra. If the corpus cavernosum is also missing, the condition is referred to as fusiform megalourethra. With the supportive tissues normally present within the shaft of the penis missing, the structure of the penis is not properly supported, allowing the urethra to expand in an unnatural fashion. This condition can be detected at birth, often resulting in an overly large, misshapen penis. Megalourethra often is accompanied by other malformations in the urogenital region, so any infant diagnosed with megalourethra should also be examined closely for other congenital defects.
AS FEATURED ON:
AS FEATURED ON:












Discussion Comments
Penis injury (ow...) such as hematomas and tears in the corpus spongiosum can occur during sex with such movements as hitting your penis on your partner's pelvic bone. However, surgery can repair the tear and this penis injury can avoid becoming an impotence cause. I wonder how common injuries like these are…
As mentioned in the article, one rare cause of corpus spongiosum damage is priapism (an erection that lasts longer than 6 hours). Priapism can also damage and typically damages another part of the penis: the corpora cavernosa.
Post your comments