At WiseGEEK, we're committed to delivering accurate, trustworthy information. Our expert-authored content is rigorously fact-checked and sourced from credible authorities. Discover how we uphold the highest standards in providing you with reliable knowledge.
What is the Axillary Artery?
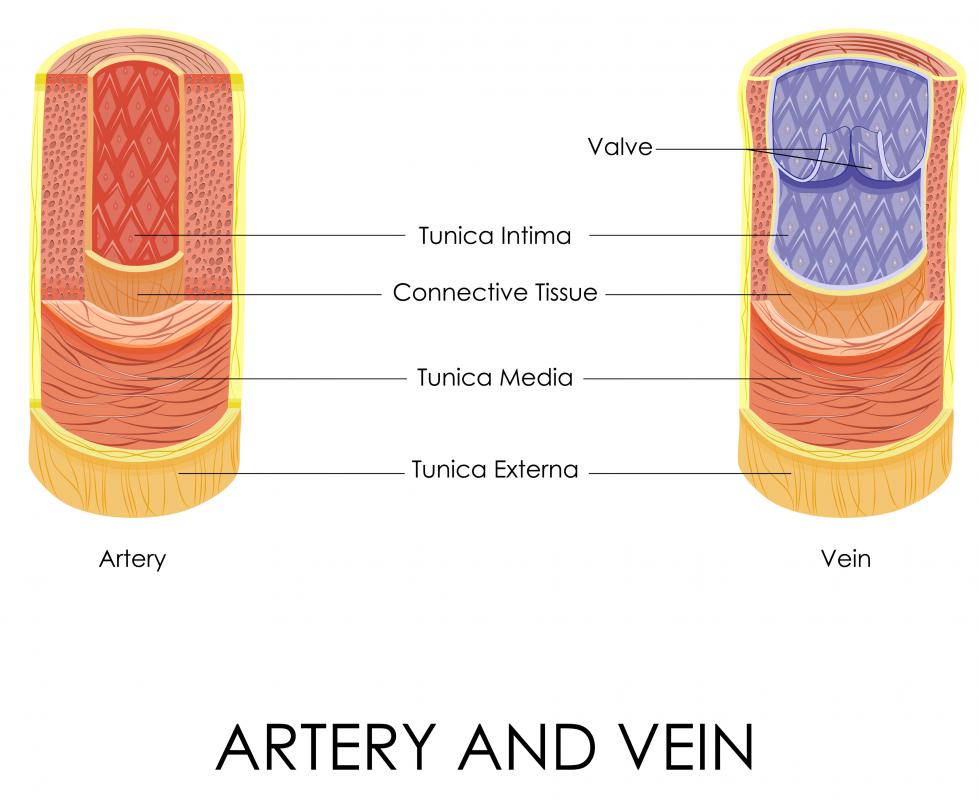
The axillary artery is a vessel that begins at a person's topmost rib and supplies the muscles of the arm with blood. This main artery is a continuation of the subclavian artery, which runs along the base of the neck before it joins the axillary. It ends where it passes the teres major muscle and becomes known as the brachial artery.
There are a number of branches dividing off from the main axillary artery. There can be as few as five branches and as many as 11, but most individuals have six of these branches. These branches supply blood to muscles such as the deltoid and to the humeral head, and some of them are wrapped around the humerus and penetrate the bone. The axillary artery and its branches supply the muscles of the arm with blood; along the artery runs the axillary vein, which brings the blood back toward the heart to be recycled.

The axillary artery has three sections, and they are defined by their location in regard to the pectoralis minor muscle; directions are given as though looking at a person's extended arm from the back. The first section runs between the junction of the axillary and subclavian arteries, ending when it reaches the edge of the pectoralis minor muscle. The second section disappears underneath the muscle, and the third section runs along the bottom edge of the remainder of the muscle.

The axillary artery is susceptible to many types of injuries because of its location partially along the underside of the pectoralis minor muscle. Injuries to the artery are often a result of some other damage; for instance, when the shoulder is dislocated, the axillary artery can stretch or even rupture. Like other arteries, there is always a risk of thrombosis. This condition, which is the creation of a potentially dangerous blood clot in the artery, can form as a result of something as simple as the improper placement of crutches and continued pressure. The impact of a blunt object can also rupture the artery.
AS FEATURED ON:
AS FEATURED ON:













Discuss this Article
Post your comments