At WiseGEEK, we're committed to delivering accurate, trustworthy information. Our expert-authored content is rigorously fact-checked and sourced from credible authorities. Discover how we uphold the highest standards in providing you with reliable knowledge.
What Is the Anterior Tibial Artery?
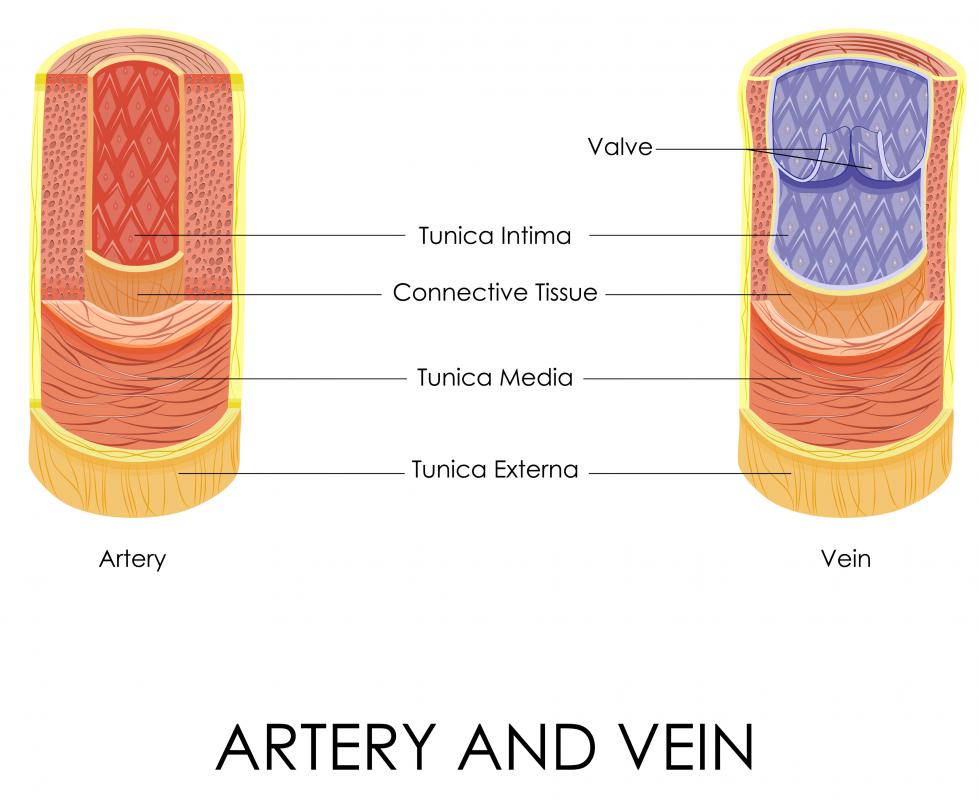
The anterior tibial artery is a major blood vessel of the leg between the knee and the ankle. It is found in the anterior compartment of the leg, which includes the structures in the lower leg found in front of the tibia and fibula bones. This vessel splits off of the popliteal artery on the posterior aspect of the knee joint and descends through the shin to the front of the fibula. The anterior tibial artery supplies blood to the skin, tissues, and muscles of the shin, including the tibialis anterior, extensor digitorum longus, and extensor hallucis longus. It also supplies the dorsal or top aspect of the foot, where it becomes the dorsalis pedis artery.
In the thigh, the major artery is the popliteal, which carries the blood that supplies vital nutrients and oxygen to the tissues of the leg. As this artery passes behind the knee, it splits into two vessels: the posterior tibial artery and anterior tibial artery. This split occurs at the height of the bottom of the popliteus muscle, which crosses the back of the knee. The significantly larger posterior tibial artery penetrates the posterior compartment of the leg, where it forms another major branch called the peroneal artery.

On the other side of the leg bones, the anterior tibial artery runs longitudinally down the leg. It sits to the front of the fibula bone, which is situated on the outside aspect of the leg. To the inside of the artery is the sheet of fibrous connective tissue between the two leg bones known as the interosseous membrane. Lateral to the anterior tibial artery are the peroneus longus and brevis muscles and the sheath of fascia surrounding them.

In front of and lateral to the artery is the deep peroneal nerve, which innervates these muscles. Directly in front of the anterior tibial artery is the anterior tibial vein. This vessel returns blood depleted of oxygen and nutrients to the lungs and heart.
Giving off several smaller branches on its course through the shin, including the fibular, tibial recurrent, and anterior malleolar arteries, the anterior tibial artery angles slightly toward the tibia bone as it descends. Crossing the front of the ankle in front of the bottom of the tibia, the artery passes beneath the horizontal ligaments known as the superior and inferior extensor retinaculi. Once it has penetrated the dorsal surface of the foot, it continues onward with a new name: the dorsalis pedis artery. This artery splits into branches of its own in the foot, the lateral and medial tarsal branches.
AS FEATURED ON:
AS FEATURED ON:











Discuss this Article
Post your comments