At WiseGEEK, we're committed to delivering accurate, trustworthy information. Our expert-authored content is rigorously fact-checked and sourced from credible authorities. Discover how we uphold the highest standards in providing you with reliable knowledge.
What is Syndactyly?
Syndactyly is from the Greek words syn, meaning "together" and daktulos, meaning "finger." It is a medical term referring to a condition in which the toes, fingers, or both have webbing in between that joins them together, most often due to genetic factors. In most cases, the webbing in syndactyly is only skin, but in some cases, the bones of two digits may be fused together. Syndactyly is the most common congenital hand symptom, occurring in one birth of every 2,500, and it is most often first noticed as a newborn is examined after birth.
This condition occurs more often in males than females, and most often in Caucausians, compared to people of Asian or African descent. There are several different underlying causes that can lead to syndactyly. Down syndrome is one of the most common causes. Rarer causes include Apert syndrome, Carpenter syndrome, Cornelia de Lange syndrome, Pfeiffer syndrome, and Smith-Lemli-Opitz syndrome. In all of these cases, syndactyly is only one of a group of interconnected symptoms.

Syndactyly by itself is often inherited, in which case it is referred to as hereditary syndactyly. The condition may also occur in combination with the presence of one or more extra fingers or toes, a condition called polydactyly. When the two conditions are combined, it is called polysyndactyly. Hereditary syndactyly is found in Angus cattle, as well as humans. While polydactyly is frequently found in cats, polysyndactyly is specific to humans.

Syndactyly can be more or less severe, and the precise situation dictates the treatment. It most frequently occurs between the third and fourth fingers. In incomplete syndactyly, fingers are only partially joined, whereas in complete syndactyly, the fingers are joined all the way to the tip. Simple syndactyly refers to webbing that is only skin and soft tissue, while complex syndactyly refers to a conjoining that includes connected bones. In complicated syndactyly, extra bones and abnormal ligament and/or tendon development is also involved.

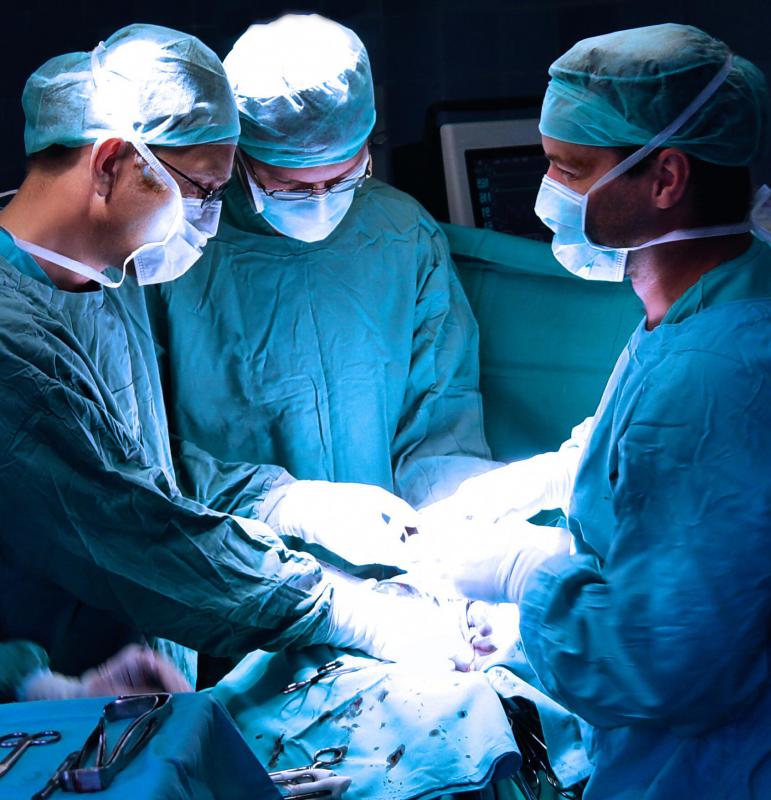
In only half the cases does syndactyly occur bilaterally; the other half of the time it is only on one hand or foot or the other, not both. Corrective surgery is usually performed when the child is as young as five to six months or between one and two years of age, according to two different sources. Earlier intervention is desirable in more difficult cases and when leaving the situation untreated would result in further problems.

In straightforward cases, the webbing between the digits is severed and skin grafts taken from the abdomen are used to minimize scarring. A cast is used after surgery both to immobilize the hand and protect the skin graft. After about three week, the cast is removed and splints are used over the next six weeks to keep the involved fingers apart. Occupational therapy helps the child improve the use of his or her hand.

In cases in which the syndactyly is isolated, the prognosis is excellent. In cases in which it is part of a syndrome, the results will depend on the child's overall condition. For example, in some cases, syndactyly is associated with cardiac problems. In such cases, the heart condition may determine when and if the child has surgery.
AS FEATURED ON:
AS FEATURED ON:















Discussion Comments
that's a good question. i wonder that, too. my uncle and i have syndactyly and i wonder if i will pass it to my kids. i love my scars and they don't bother me. if your children's kids do get it, just have them have surgery to correct it. that's what my parents did for me when i was 2 1/2 years old. now I'm 15 and i love that i can play piano and bassoon. i had this trait on both feet and left hand.
my husband's grandma his dad and he all have syndactyly. his grandmas toes, his dad's two fingers on both hands and both feet, and he has three fingers on one hand and two fingers on the other and both toes. Our two children however show no signs of it. If and when they have children will they be able to pass it on to their children?
Post your comments