At WiseGEEK, we're committed to delivering accurate, trustworthy information. Our expert-authored content is rigorously fact-checked and sourced from credible authorities. Discover how we uphold the highest standards in providing you with reliable knowledge.
What Is Nodular Fasciitis?
Nodular fasciitis refers to a condition where a benign growth occurs under the skin, in the muscle, or in the connective tissues. This may have few symptoms, though in about half of the cases, there may be some tenderness when the growth is touched. Doctors suggest that injury to the tissues may be a possible cause of this condition. Since the node may rapidly increase in size, it is sometimes misdiagnosed as a cancerous sarcoma, and scans or a biopsy might be performed to rule this out. Treatment may then consist of watching the node for further developments or surgically removing it.
The types of material that may make up a nodular fasciitis growth may include water, fibers, or mucous. These tend to develop as a response to some external injury or to inflammation occurring within the body. Sometimes they occur in the absence of a clear cause.

Commonly, growths form right below the skin, but sometimes these benign tumors develop in the muscles or joints, too. Muscular nodular fasciitis lesions tend to grow quickest and are most likely to resemble sarcomas. The size of these nodes can vary, and they may be anywhere from a few hundredths of an inch (a few millimeters) to 0.39 - 1.97 inches (1 - 5 centimeters) in diameter.

Although the cause isn’t always clear, it’s known that nodular fasciitis can occur in children or adults, and most often affects people in the early decades of adulthood. If kids develop this condition they often get growths on the head or neck. Conversely, nodes tend to most often occur on forearms in adults. In adulthood, both genders develop these growths with equal frequency, but male children are more likely to get them than female children. Nodular fasciitis does not always develop in the most expected places or ways and reports exist of rare cases where it developed on the breasts, back, and legs or exceeded the expected size.

Symptoms of this condition may include a perceptible lump, possibly following injury or inflammation. Sometimes this lump is swollen or painful, but about half of people with nodular fasciitis experience no discomfort. Any rapidly expanding growth requires medical attention to rule out malignancies.
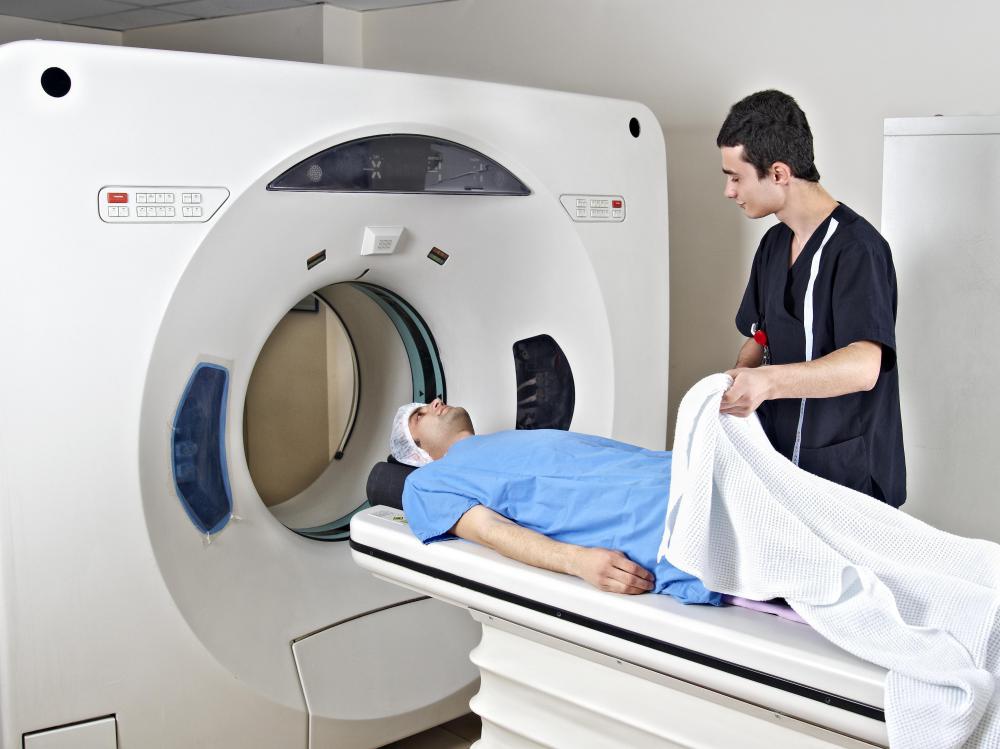
Doctors can’t tell by feeling a lump if it is benign or malignant. Instead, they may opt to do scans like magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or a computerized tomography (CT) scan. These alone can’t indicate whether a growth is nodular fasciitis or some other condition that is more dangerous. The best method to determine this is to biopsy the node.

Once a growth has been identified as nodular fasciitis, doctors may opt not to treat it, since these sometimes resolve without intervention. Alternately, the whole node may be removed, which is a good option if it is causing discomfort or if the growth is unsightly. Many patients respond well to excision, and over 90% of individuals experience no recurrence. Treatment is typically performed on an outpatient basis, and individuals are quickly able to resume normal activities.
AS FEATURED ON:
AS FEATURED ON:















Discuss this Article
Post your comments