At WiseGEEK, we're committed to delivering accurate, trustworthy information. Our expert-authored content is rigorously fact-checked and sourced from credible authorities. Discover how we uphold the highest standards in providing you with reliable knowledge.
What is Hyperkalemia?
Hyperkalemia is a medical condition characterized by elevated levels of potassium in the blood. Depending on the amount of potassium involved, this condition can be life threatening, and it requires medical treatment to eliminate the excess potassium and uncover the underlying cause. Many people discover that they have hyperkalemia in a routine medical examination, when blood testing reveals unusually high levels of potassium in the blood. Early detection can prevent long-term problems.
Broken down into its root words, “hyperkalemia” literally means “excessive potassium in the blood.” A number of things can lead to this condition, including kidney failure, the use of certain medications, problems with the adrenal glands, excessive intake of potassium, and conditions which cause the cells to release potassium such as a medical problem which leads to widespread cell death. Under normal conditions, the body regulates potassium levels by expressing potassium in the urine, uptaking potassium in the cells, or vomiting when too much potassium has been consumed.

Potassium is an important mineral in the body. It helps to regulate muscle movement, which is why people recommend taking potassium for muscle cramps, as the increased potassium can help the muscle relax. However, when potassium levels get too high, they can cause problems with muscle function, leading to muscle weakness and fatigue. Most critically, excessive potassium leads to arrhythmias, eventually causing a heart attack. In fact, the mineral is so good at causing heart attacks that potassium chloride is used in lethal injections.

When a patient presents with hyperkalemia, the first goal is to get potassium levels down. In a mild case, the patient may switch to a low-potassium diet and the doctor may review the patient's medical history and lifestyle to look for causes. For example, the condition could indicate the presence of an underlying medical problem, or the patient might just be eating way too many bananas. Follow-up testing may be used to ensure that potassium levels are lowered.

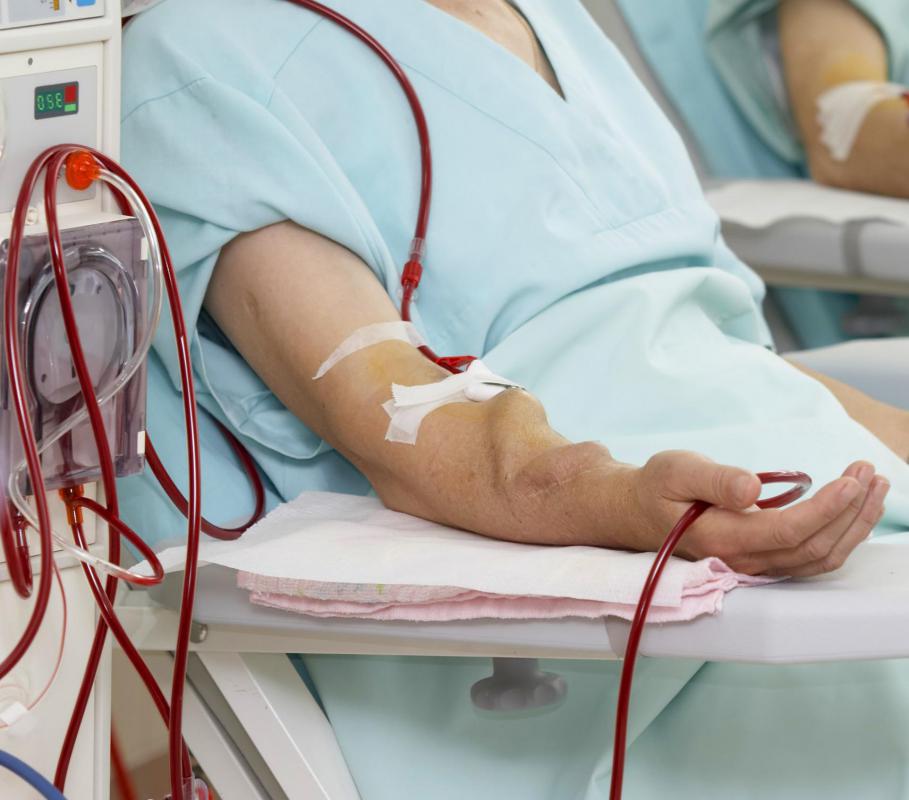
In acute hyperkalemia, potassium levels may be lowered with the use of a variety of medications, or even dialysis to flush potassium out of the blood. In addition, the patient may be given calcium to help regulate his or her heart beat, ensuring that heart failure does not occur while the patient is undergoing treatment. Once the patient is stabilized, the doctor can look for the root cause of the hyperkalemia and address it so that potassium levels will not rise again.
AS FEATURED ON:
AS FEATURED ON:
















Discussion Comments
Also a mistake in this article. The body regulates potassium levels by EXCRETING potassium in the urine, not expressing.
Overall good summary, thanks.
High K+ levels (high enough to diagnose hyperkalemia) are 5.5 mEq/L and above. The normal range is 3.5-5.0.
I would like to know what the numbers are that indicate high potassium. How high above the "normal" range is considered dangerously high?
so- 1) I had a triple bypass over 2 years ago,and 2)it sounds like the banana/potassium overdose may be the reason for my high potassium count. I am still worried about my heart; how do I know if it has been affected by the potassium? Will stopping the bananas make a measurable difference, and in what time frame?
Post your comments