At WiseGEEK, we're committed to delivering accurate, trustworthy information. Our expert-authored content is rigorously fact-checked and sourced from credible authorities. Discover how we uphold the highest standards in providing you with reliable knowledge.
What is Bacterial Endocarditis?
Bacterial endocarditis, more commonly referred to as infective endocarditis, is an infection of the heart valves or lining of the heart chambers. It occurs when bacteria from the mouth, skin, upper respiratory system, intestinal tract or urinary tract enters the bloodstream and attaches to the heart. People with preexisting heart conditions tend to be most at risk for developing the infections because their heart lining tends to be rougher, making it easier for bacteria to stick. Bacterial endocarditis can lead to permanent heart damage or death if untreated.
Certain procedures, such as dental cleaning, or gastrointestinal or urinary tract procedures, can cause bacteria found in those areas to briefly travel into the bloodstream. People with heart conditions, such as congenital heart defects, artificial hearts, or damaged heart valves, are more likely to have the bacteria cause infection because the body produces various cells to repair their heart damages. Bacteria can become trapped under the extra cells and form clumps of infected tissue called vegetations. Vegetations can travel throughout the bloodstream and block blood vessels or spread the infection to other parts of the body, such as kidneys, brain, or lungs.

Intravenous drug users are also at risk for developing bacterial endocarditis. Using dirty needles can inject bacteria directly into the bloodstream. Drug users are also at a higher risk of having human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), which increases the chances of the infection not responding to treatment.
Symptoms of bacterial endocarditis are similar to the flu, which may prevent some people from seeking treatment. One of the most common symptoms of the infection is a fever that lasts for over three days. The infection also can causes extreme fatigue, loss of appetite, and fatigue. In more severe cases, joint pain, bright red skin rash, wounds that won’t heal, and bloody or discolored urine may also occur.
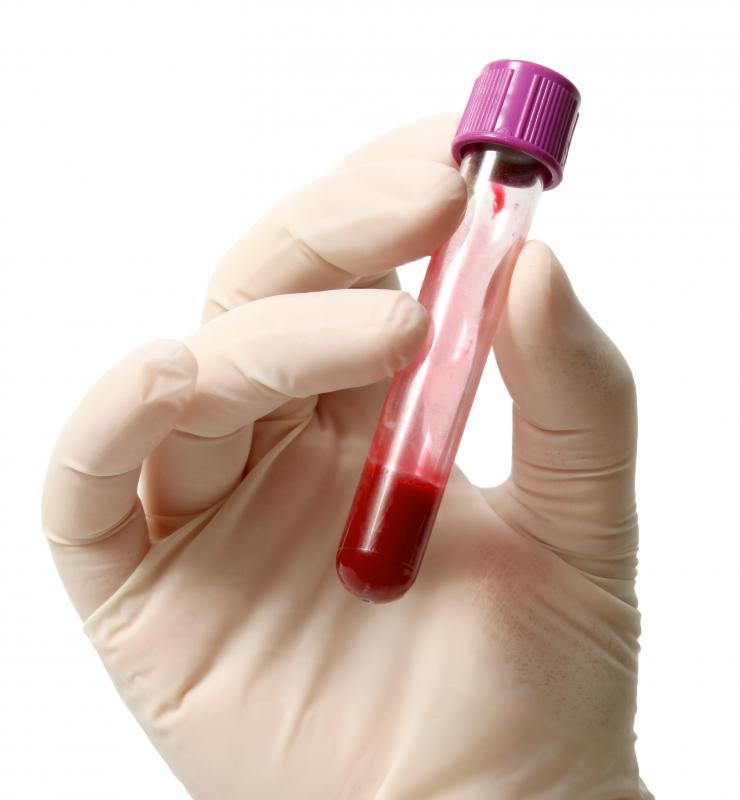
Doctors generally diagnose the infection by performing a blood culture. Blood samples are combined with solutions that make any bacteria visible. An ultrasound of the heart called an echocardiogram can also be run to check for signs of infection.

Serious complications can arise from the infection, such as irregular heartbeat, blood clots, infection of the brain, stroke, and heart failure; however, bacterial endocarditis is usually treatable if reported to doctors in time. A person with the infection is typically given intravenous doses of antibiotics for approximately four to six weeks to fight the bacteria. Surgery may also be performed if the infection caused additional damage to heart valves or lining.

There are some ways to prevent bacterial endocarditis. People with preexisting heart conditions may be advised to take antibiotics prior to dental or other medical procedures to fight off the bacteria before it spreads. Oral hygiene and proper care of cuts or wounds may also reduce the risk of bacterial endocarditis.
AS FEATURED ON:
AS FEATURED ON:












Discuss this Article
Post your comments