At TheHealthBoard, we're committed to delivering accurate, trustworthy information. Our expert-authored content is rigorously fact-checked and sourced from credible authorities. Discover how we uphold the highest standards in providing you with reliable knowledge.
What is a Saline Bolus?
When a person has lost a lot of blood, action needs to be taken immediately. The patient's blood pressure needs to be raised as soon as possible to eliminate the possibility that he will go into circulatory shock, which can be fatal. One method to raise blood pressure quickly is by introducing a large amount of saline into the person’s veins. Medical professionals do this by administering a saline bolus, a rapid injection of a large amount of saline.
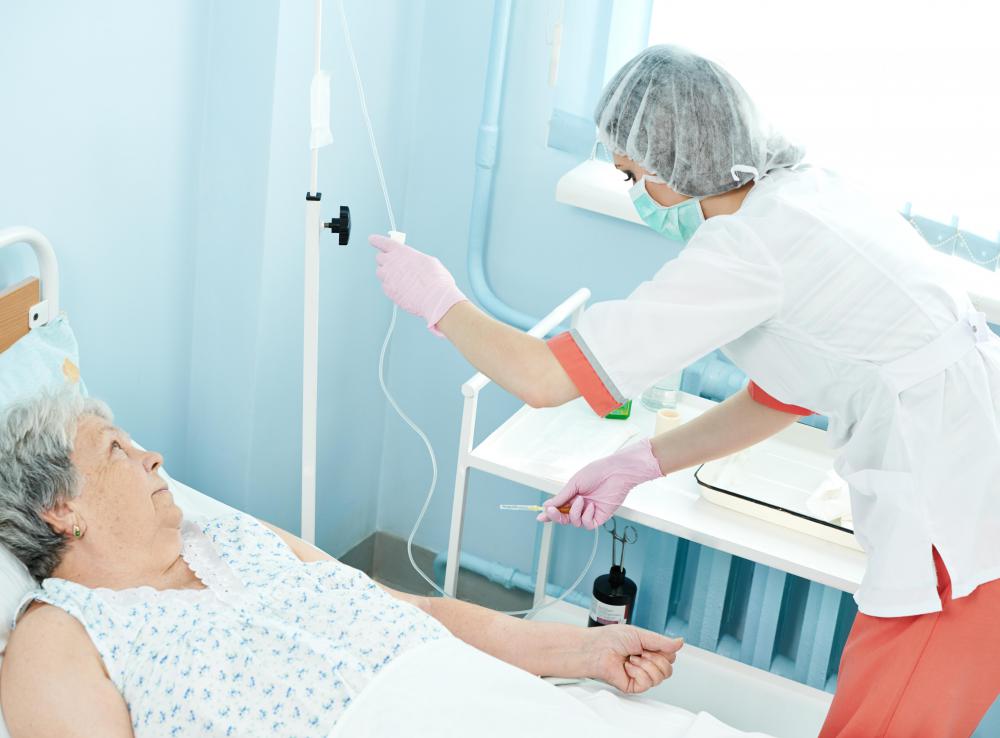
Intravenous (IV) medication administration is a process in which medications are given to a patient by inserting a needle directly into the vein and injecting the medicine. Medications or liquids can be administered quickly by using a syringe or slowly by using a bag that drips medication through an IV line and into the patient’s vein. Squeezing the bag manually or using special tools can quickly push the liquid through the IV line to administer a bolus.

Saline is often administered to patients to bring up their blood pressure. When a person suffers blood loss, his blood pressure drops drastically. The lack of blood pressure means blood has difficulty reaching the body’s vital organs, which can lead to shock. Pumping saline into the person’s circulation system increases blood pressure so blood continues circulating through the body’s organs. It buys the patient time until a blood transfusion can replace blood that has been lost or, in the case of infections, antibiotic treatment can be administered and begin working.

There are three different types of shock: hypovolemic, distributive, and cardiogenic. In hypovolemic shock, at least one-fifth of the body’s blood supply is lost quickly through bleeding or vomiting, and the heart isn’t getting enough blood to supply it to the organs, which start shutting down as a result. Distributive shock is the result of the body’s blood vessels dilating and is most often caused by an infection, such as sepsis. The third, cardiogenic shock, is caused by failure of the heart to adequately pump blood throughout the body. Saline boluses are generally given for hypovolemic and distributive shock, but not for cardiogenic shock.

There are other reasons to administer a saline bolus, but preventing shock is one of the most important. Medical personnel can save lives with a timely administration of a saline bolus. This makes the saline bolus an important tool in the medical arsenal.
AS FEATURED ON:
AS FEATURED ON:















Discussion Comments
@bythewell - While, I'm sure that coconut juice can be used as a saline bolus, a bolus of saline means that saline was administered quickly, rather than put in slowly.
Saline solution might be given to a patient in a drip feed without it being a "bolus". Normally, a saline IV bolus is given when there is an emergency and they have to push the fluid into the bloodstream as quickly as possible.
Just making sure you knew the distinction.
One of those random facts that I picked up somewhere... coconut juice can be used like a saline bolus. Actually, I never knew what it was called when someone gives you fluid as an emergency method to replace blood.
Apparently they used to use coconuts when they ran out of plasma in wars. They would just hook up the IV but instead of using normal saline boluses they would use coconut juice instead.
It's sterile because it comes from inside the coconut, and I think that is the reason they use it, rather than because it's similar to blood chemistry or anything. But, you never know when this might come in handy!
Post your comments