At TheHealthBoard, we're committed to delivering accurate, trustworthy information. Our expert-authored content is rigorously fact-checked and sourced from credible authorities. Discover how we uphold the highest standards in providing you with reliable knowledge.
What Is a Non-Sedating Antihistamine?
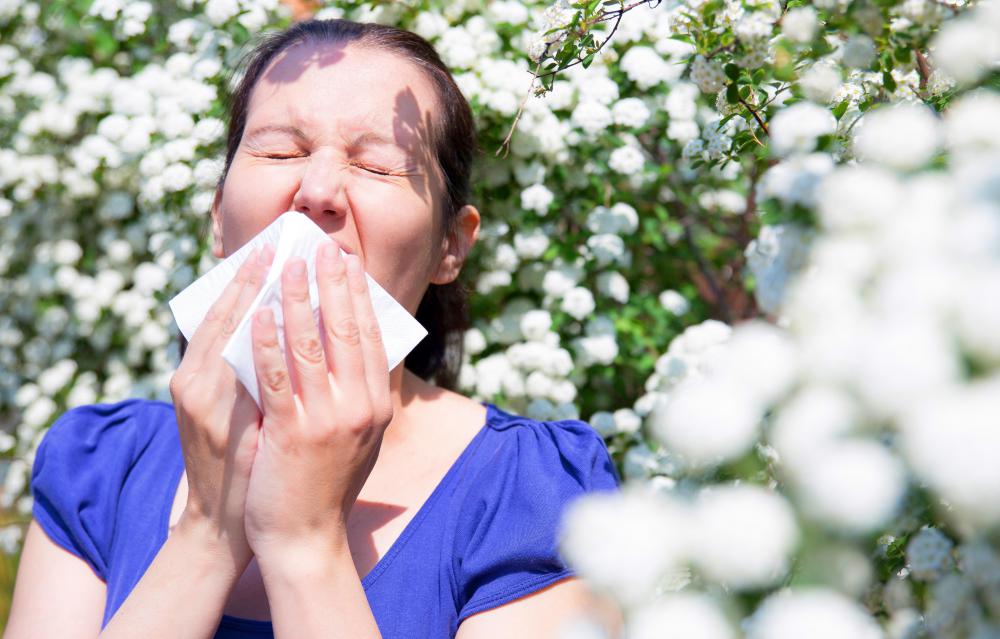
When the body comes into contact with something to which it is allergic, whether through contact, respiration or consumption, substances called histamines are released to attack the allergen. Histamines encourage the body to rid itself of the allergen by triggering ways to flush the allergen, such as watery eyes, a runny nose and sneezing; if the skin is the affected area, the histamines may produce a rash as protection. Antihistamines block histamines, thereby preventing some or all of the allergen's effects, but early antihistamines often caused drowsiness. A non-sedating antihistamine is one that is less likely to cause patients to feel sleepy or tired.
Although pharmaceutical manufacturers describe some of their products as non-sedating antihistamines, some patients do experience drowsiness, fatigue, impaired motor responses and concentration difficulties when taking them. On the other hand, some patients experience none of these symptoms when taking sedating antihistamines. Because each patient can react differently, individuals should determine how they react to a non-sedating antihistamine before driving, taking important tests or operating dangerous machinery.

Many types of antihistamines are available without a prescription. Examples of over-the-counter non-sedating antihistamines include the brand names Claritin®, Allegra®, and Zyrtec®. Most are available as just an antihistamine or in combination with other drugs such as decongestants. Prescription non-sedating antihistamines include Clarinex® tablets and the nasal spray, Astelin®.

Over the years, many uses of antihistamines have been discovered. Many patients are most familiar with antihistamines used to treat respiratory allergies such as hay fever or as an ingredient in over-the-counter sleeping pills. Others antihistamines, such as meclizine, are often prescribed to prevent the vertigo and nausea that accompany motion sickness. When suffering from a cold or flu, some patients find that antihistamines help dry the nasal secretions and relieve the cough. Occasionally, certain antihistamines are used to treat chronic headaches or asthma.

Side effects of antihistamines depend in part on the specific type. The most common potential side effects include headache, digestive problems, aching muscles and fatigue. A non-sedating antihistamine can, in rare instances, cause convulsions, lightheadedness, irregular heartbeats and jaundice. Some patients taking a non-sedating antihistamine have reported that the medication made them hyperactive or prevented them from falling asleep at night.

In addition, it is possible for a patient to be allergic to the medication itself, whether it is a sedating or non-sedating antihistamine. Patients taking an antihistamine should receive immediate medical care if they have difficulty breathing or swallowing, develop hives, or if they experience any internal or external facial swelling. If the heart rate is uneven or fast, or if the patient is shaking and weak, the medication should be stopped and the patient's physician notified immediately.
AS FEATURED ON:
AS FEATURED ON:















Discuss this Article
Post your comments