At AllThingsNature, we're committed to delivering accurate, trustworthy information. Our expert-authored content is rigorously fact-checked and sourced from credible authorities. Discover how we uphold the highest standards in providing you with reliable knowledge.
What is a Mammal?
A mammal is member of the Mammalia class of animals, and includes many familiar creatures, including humans. There are more than 5,000 species, most of which live on land, excluding a few species such as dolphins, whales, and manatees. A mammal can be recognized by a series of unique characteristics, which include the following:
- Mammary glands. A mammal can produce milk to feed its young, as opposed to other species, which feed their offspring with solid food. Young are born alive, except for a few species, such as species in the monotremes order, which lay eggs.
- Warm blood. Animals in this class have warm blood, which helps them maintain steady body temperature. They also have a heart with four chambers, a unique characteristic that allows the lungs to receive oxygenated blood in proper amounts. These animals have bodies that are all covered with some kind of hair or fur that helps with heat preservation, and even aquatic mammals have hair at some point during their life.
- Neocortex. A mammal posses a brain section that does not occur in any other animal class. The neocortex is the section that controls language, motor commands, and conscious thought. While birds and certain reptiles seem capable of experiencing some of these characteristics, the neocortex is still unique to mammals.
- Size. Mammals have the largest difference between the smallest (bats) and the largest (blue whale) species: a 53 million-fold. No other animals come even close in comparison.
- Skeleton. Animals in this class have fewer bones than other animal classes; they also have a rigid rib cage, solid hip attachments, specialized adapted teeth, simplified limbs, and increased size of the brain case.
- Adipose tissue. Mammals have a larger percentage of fat deposits than any other animal class; this helps them with energy storage and thermal insulation. A mammal can survive a longer time without food or water than any other species on Earth.
Frequently Asked Questions
What defines an animal as a mammal?
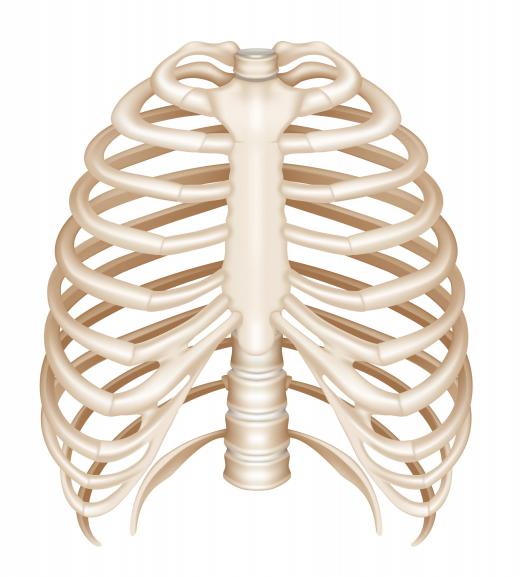
A mammal is characterized by several key features: they are warm-blooded vertebrates, have hair or fur, produce milk to feed their young through mammary glands, and most give birth to live young. Additionally, mammals have a unique jaw structure and three middle ear bones, which contribute to their distinct classification in the animal kingdom.
How do mammals regulate their body temperature?

Mammals are endothermic, or warm-blooded, meaning they maintain a constant body temperature regardless of the environment. They achieve this through metabolic processes that generate heat, as well as physical adaptations like fur for insulation. Some mammals also exhibit behaviors such as basking in the sun or seeking shade to assist in thermoregulation.
Are all mammals land-dwelling creatures?

No, not all mammals are land-dwellers. While many mammals thrive on land, there are also aquatic species like whales and dolphins, and semi-aquatic species such as otters and beavers. These mammals have adapted to their environments with specialized limbs for swimming and the ability to hold their breath underwater for extended periods.
What is the largest group of mammals?

The largest group of mammals is the Rodentia, or rodents, which includes over 2,000 species, accounting for roughly 40% of all mammalian species. This diverse group ranges from the tiny African pygmy mouse to the sizable capybara, and they are found in a variety of habitats across the globe.
How do mammals contribute to their ecosystems?
Mammals play crucial roles in their ecosystems, such as pollinators, seed dispersers, predators, and prey. They help maintain ecological balance by controlling insect populations, dispersing seeds that lead to forest regeneration, and providing nutrients to the soil through their waste. Their interactions within food webs are essential for the health of many ecosystems.
What is the most intelligent mammal and why?

The most intelligent mammal is widely considered to be the human, due to our complex language, problem-solving abilities, and advanced use of tools. However, other mammals like dolphins, elephants, and certain primates also exhibit high levels of intelligence, demonstrated by their social structures, communication skills, and ability to learn and adapt to new challenges.
AS FEATURED ON:
AS FEATURED ON:


















Discussion Comments
@ Georgesplane- Are you ready for this? The news you ask for is sobering. Of the approximately 5500 mammal species, 22% are threatened on the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) red list. This includes many iconic species like the lion, snow leopard, cheetah, tiger, elephant and other mammals. To be placed on the red list, a species must be threatened, endangered, or critically endangered. Some of the greatest species are down to populations that rank in the hundreds, and hundreds of mammal species (a couple percent) will likely to be extinct within a generation. This loss of biodiversity far outpaces the speed of evolutionary processes.
If you need a more sobering perspective, off all the major species in the world, the IUCN has identified 38% of them as threatened, endangered, or critically endangered. Another small percentage of all species is extinct in the wild, or have gone extinct altogether.
Although some may point out that conservation efforts have reduced the number of species on the red list, you must also take into consideration that 86% of the species on the list that changed from 2007-2008 moved closer to extinction. A sterile world with very little biodiversity is an extreme possibility within the next few hundred to thousand years.
@ babalaas- Does anyone know what the number of endangered mammal species is? I am curious to know if mammal evolution is occurring faster than they are going extinct. I wonder if the rate of extinction is anywhere near sustainable, or if we are slowly marching towards a planet devoid of biodiversity. I read about a lot of controversy concerning biodiversity loss, and I am just trying to gauge how serious of a threat it is.
This is a great article. The article was short and to the point. One fact that surprised me was the bit about the total number of species. I would have thought that there were far more than 5400 species. After reading that number, the prospect of losing a mammal species to human caused extinction much more upsetting. I would have thought that there would have been somewhere in the tens to hundreds of thousands of species of mammals. I now have a greater appreciation of endangered mammals.
Post your comments