At WiseGEEK, we're committed to delivering accurate, trustworthy information. Our expert-authored content is rigorously fact-checked and sourced from credible authorities. Discover how we uphold the highest standards in providing you with reliable knowledge.
What is a Geniculate Nucleus?
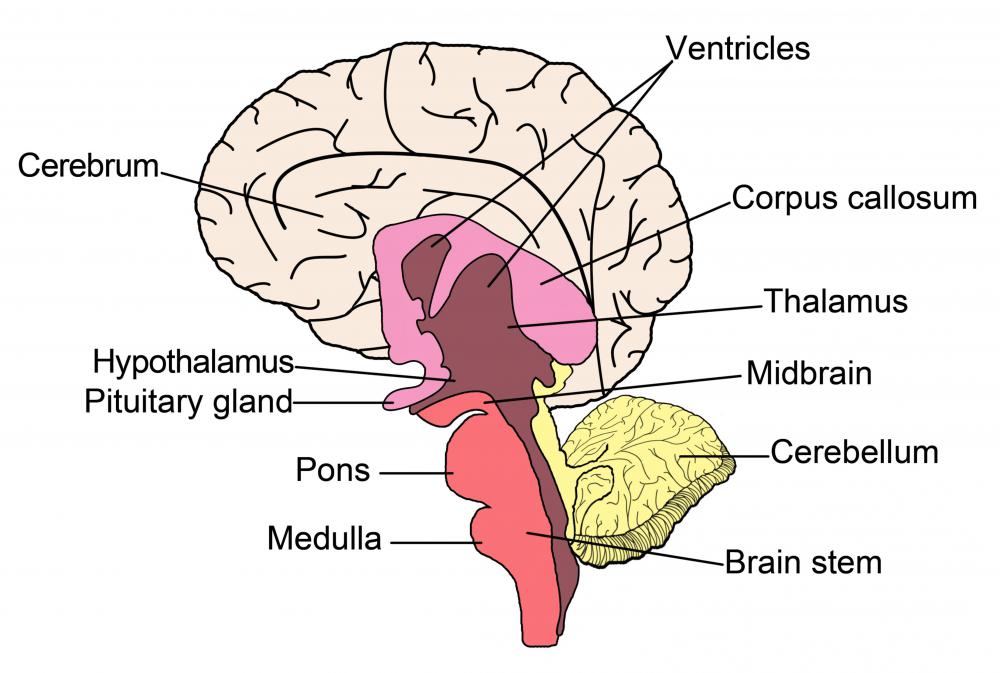
The thalamus is a part of the brain that acts as a relay for sensory information, receiving information from the sensory organs and sending it to the cerebral cortex for higher level processing. The geniculate nucleus is a part of the thalamus that relays auditory and visual information. It is divided into two parts: medial and lateral. The medial part is involved in auditory processing and the lateral part relays visual information.
The thalamus receives information from all of the senses except for smell. It acts as a gatekeeper for sensory information, determining what information is passed on to the cortex. The cortex also sends return projections back to the thalamus.

The thalamus has many other functions besides acting as a relay for sensory information. It regulates sleep and wakefulness, and also plays a role in consciousness. It sends signals to the cortex, which in turn sends signals back to the thalamus. These loops play a role in regulating arousal and activity. The thalamus also plays a role in motor functions and movement.

The thalamus is made up of many different nuclei, which are divided into subgroups based on location. Different nuclei have different functions, and connect to different parts of the brain. The geniculate nucleus is located in the posterior group of thalamic nuclei.
Sound waves in the air travel into the ear, where they are transformed into electrical signals. These signals travel through several structures, such as the cochlear nucleus and superior olivary complex, finally ending up at the inferior colliculus. This structure integrates information about sound localization.

The medial geniculate nucleus receives information about sounds from the inferior colliculus. This information is organized tonotopically, which means it is spread out spatially based on the frequency of the noise. This information travels from the thalamus to the superior temporal gyrus, located in the temporal lobe of the brain.
The retina, located in the eye, turns light signals into electrical impulses that are then carried to the brain by the optic nerve. The lateral geniculate nucleus receives this visual information. This structure is divided into six layers, and different layers receive different types of information from the eye.
Visual information is then relayed to the primary visual cortex in the occipital lobe. This structure is located in the back of the brain, and processes information about edges, colors, and motion. It also sends return projections back to the lateral geniculate nucleus.
AS FEATURED ON:
AS FEATURED ON:












Discuss this Article
Post your comments