At AllThingsNature, we're committed to delivering accurate, trustworthy information. Our expert-authored content is rigorously fact-checked and sourced from credible authorities. Discover how we uphold the highest standards in providing you with reliable knowledge.
What is a Funnel Web Spider?
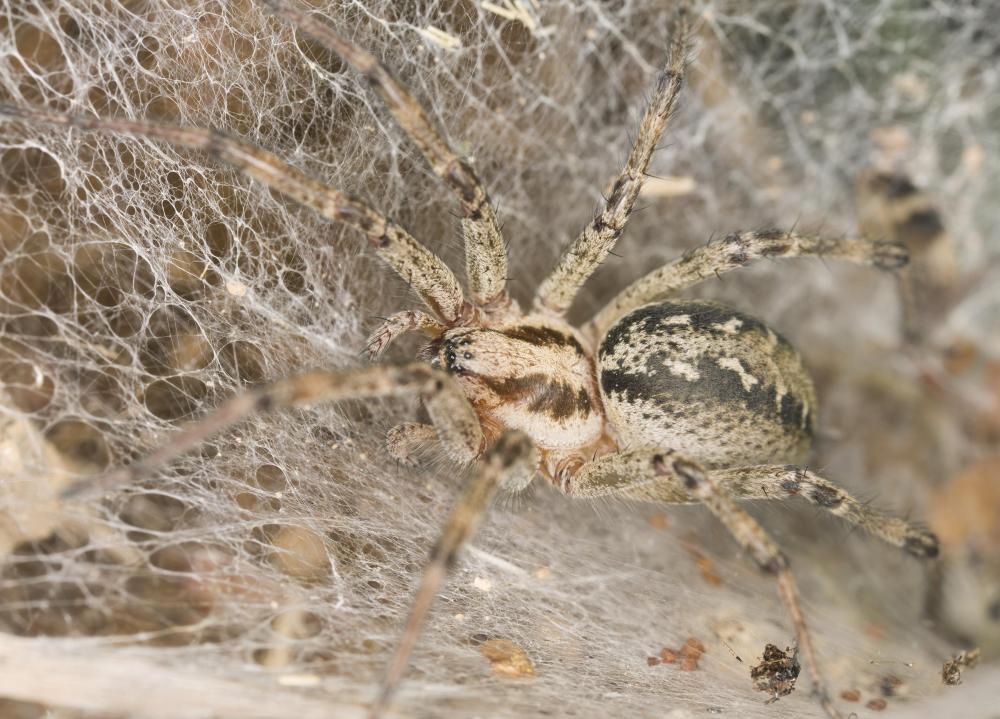
The funnel web spider refers to 36 species of spiders, which are indigenous to Australia. These arachnids tend to live in burrows, though a few species are tree dwellers. Some of the species are considered to be the most poisonous spiders on the earth, particularly to humans. Their venom is a powerful neurotoxin, which can, when injected through a bite, cause death if a person with a bite does not use antivenin, which is also known as antivenom. Fortunately, antivenin was quickly developed and is very effective. Since antivenin's inception, there has not been a reported death from a funnel web spider bite.
The funnel web spider is a large specimen of arachnid. Their body length can range from half an inch to 1.75 inches (1.5-4.5 cm). They are usually glossy black or brown, with a smallish head, and large body cavity, resembling the black widow, though they are kin to Wolf spiders. They also are very long-lived spiders, with females that can live for up to 10 years. The males unfortunately, are consumed by the female funnel web spider after mating occurs.

In fact, most bite incidents are a direct result of funnel web spider males looking for mates and wandering into human habitats, like garages or sheds. Unfortunately, the male is more lethal than the female, and their bites are more severe. When the male funnel web spider does not inadvertently come across humans, it lives for approximately 2-4 years, depending upon when it reaches sexual maturity, which can vary depending upon species.

Unlike many spiders, the funnel web spider will spend a long time in its place of birth, usually staying for up to 2 years after the egg sac has opened. This is uncommon among spiders, as many of them quickly leave their nest site. This habit may be attributed to their long lives, which are some of the longest on record.
The spider is quite easy to recognize because of the funnel web shape it builds around its burrow. The cylindrical shaping is an important warning to stay well away from a web of this kind. The web shape also forms an important means of catching insects, as the creature entangled in the funnel cannot simply get out. If it manages to free itself from the web, it will still be surround by webs on all sides.

Although insects account for the majority of the funnel web spider's diet, researchers have also documented the funnel web spider consuming small frogs and lizards, which are ready targets if they climb into a web. Even though the thought of this spider can give many of us a chill down our spines, like most poisonous spiders, it is extremely beneficial to its environment and indirectly to humans. With insect consumption comes a reduction in insects that can spread disease among humans on a larger scale than the very occasional contact with a spider.
Should you be in Australia, whether as a resident or a visitor, it is important to note that it is very important not to threaten a funnel web spider in any way. They are very territorial, and very aggressive, and will stand their ground in a fight despite a huge size difference in anything or anyone that threatens them. If you think you have contracted a bite, it is important to seek medical attention immediately or call for emergency help, as treatment is essential.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a Funnel Web Spider?
A Funnel Web Spider is a member of the family Hexathelidae, known for its distinctive web structure that features a funnel-like retreat where the spider hides. These spiders are notorious for their potent venom, with some species like the Sydney Funnel Web being highly venomous to humans. They are primarily found in Australia and are characterized by their glossy, dark color and robust build.
How dangerous is the Funnel Web Spider to humans?
The danger of a Funnel Web Spider to humans can be significant. The Sydney Funnel Web Spider, in particular, has venom that can be lethal if not treated. However, since the introduction of antivenom in 1981, there have been no recorded fatalities. Bites should be considered a medical emergency, and immediate treatment is crucial for survival.
Where can you find Funnel Web Spiders?
Funnel Web Spiders are predominantly found in Australia, with species like the Sydney Funnel Web inhabiting the eastern coast, from New South Wales to Queensland. They prefer moist, cool habitats and can often be found in suburban areas, hiding under logs, rocks, or in burrows.
What does a Funnel Web Spider's web look like?
A Funnel Web Spider's web is easily recognizable by its unique structure. It consists of a dense, irregular silk mat with a funnel-like burrow where the spider resides. The funnel leads deep into a crevice or hole, serving as a hideout for the spider and a trap for prey, which gets entangled in the sticky surface of the web.
How does the Funnel Web Spider catch its prey?
The Funnel Web Spider employs a sit-and-wait strategy to catch its prey. It remains hidden within the funnel of its web, sensing vibrations through the silk strands. When an insect or other small creature disturbs the web, the spider quickly emerges to capture and envenomate its prey, dragging it back into the funnel to consume.
What should you do if you encounter a Funnel Web Spider?
If you encounter a Funnel Web Spider, it's important to maintain a safe distance and avoid provoking it. If indoors, safely capture it by placing a glass jar over it and sliding stiff cardboard underneath before releasing it away from the house. In areas where Funnel Web Spiders are common, wear gloves when gardening and check shoes before wearing them.
AS FEATURED ON:
AS FEATURED ON:












Discussion Comments
Having lived in Australia as a kid I can honestly say I was most frightened of the Funnel Web.
They're that horrible combination of large(ish) and deadly, though my Dad eased my fears of this by telling me about the Redback, which is a fifth of the size but likes to hide under the toilet seat...
Post your comments