At TheHealthBoard, we're committed to delivering accurate, trustworthy information. Our expert-authored content is rigorously fact-checked and sourced from credible authorities. Discover how we uphold the highest standards in providing you with reliable knowledge.
What is a Coronary Artery?
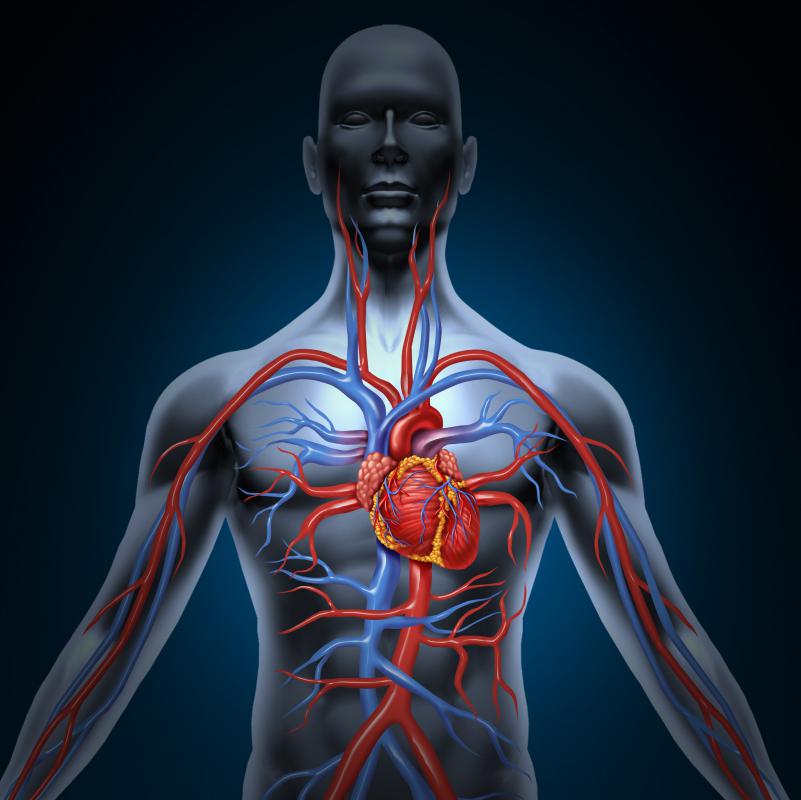
The arteries are a major part of the circulatory system in the body, tasked with carrying blood away from the heart to supply the rest of the body. A coronary artery works to supply the heart muscle itself with blood, ensuring that it functions normally and contributing to efficient blood circulation. The coronary arteries are sturdy blood vessels, but nonetheless can be subject to weakening and loss of function due to disease, unhealthy lifestyles, or simply age.
The coronary artery system is often divided into two major arteries that branch off the aorta, the main blood vessel that takes blood away from the heart. The right coronary artery brings blood to the upper right chamber of the heart, while the left brings blood to the upper left chamber of the heart. One, or occasionally both, arteries also connect to a central heart artery called the posterior interventricular artery. If the right coronary vessel attaches to this artery, the system is called “right dominant.” Statistics vary, but most experts suggest that a large majority of humans have a right dominant heart. The remaining group have hearts that join the left coronary vessel to the posterior interventricular artery, or that have both coronary arteries attached and sharing the function.

Damage or blockage of the coronary arteries is a major health concern, as the heart cannot function without an adequate blood supply. Since the heart is the major source of oxygenated blood for the entire body, serious damage to the coronary arteries can quickly lead to dangerous and fatal complications. The most common health problem involving this vital circulatory component is called coronary artery disease, or CAD.

CAD is the leading cause of death in the United States, and it, as well as associated conditions, are considered to be leading causes of death worldwide. The disease is characterized by a narrowing of the arteries and blockages caused by the build-up of fatty tissue. Some conditions associated with CAD include hypertension or high blood pressure, angina, and heart attacks.

The thinning and buildup that result in complications to the coronary arteries can be the result of a variety of factors. Doctors suggest that lifestyle, genetics and even environment can all contribute to the development of CAD. Additionally, since the disease typically develops very slowly, the first sign of coronary artery disease may be a life-threatening or even fatal heart attack. Some people are believed to be at higher risk for developing artery blockages like CAD, including diabetics, smokers, those with high blood pressure or high cholesterol levels, and people that are considered obese.

Depending on the presence of risk-increasing factors or symptoms such as high blood pressure chest pain, doctors may run several diagnostic tests to find if CAD is present and determine a proper course of action. These tests may measure heart rate in rest and activity, or check that the amount of blood pumping through the muscle is adequate. If CAD does appear to be affecting heart function, there are many treatment options available.

Lifestyle changes, such as quitting smoking, losing weight, and maintaining a healthy diet and exercise regimen, are often recommended to prevent further damage. Doctors also have a variety of drugs available to treat the condition and reduce the potential for possibly fatal complications such as heart attack. Some surgeries also exist that can clear blockage out of the arteries or allow alternate blood passageways to the heart. Although many of these treatments carry risks, successful procedures can lead to increased coronary artery function and help ensure a healthier future.
AS FEATURED ON:
AS FEATURED ON:














Discuss this Article
Post your comments