At TheHealthBoard, we're committed to delivering accurate, trustworthy information. Our expert-authored content is rigorously fact-checked and sourced from credible authorities. Discover how we uphold the highest standards in providing you with reliable knowledge.
What is a Bronchogenic Cyst?
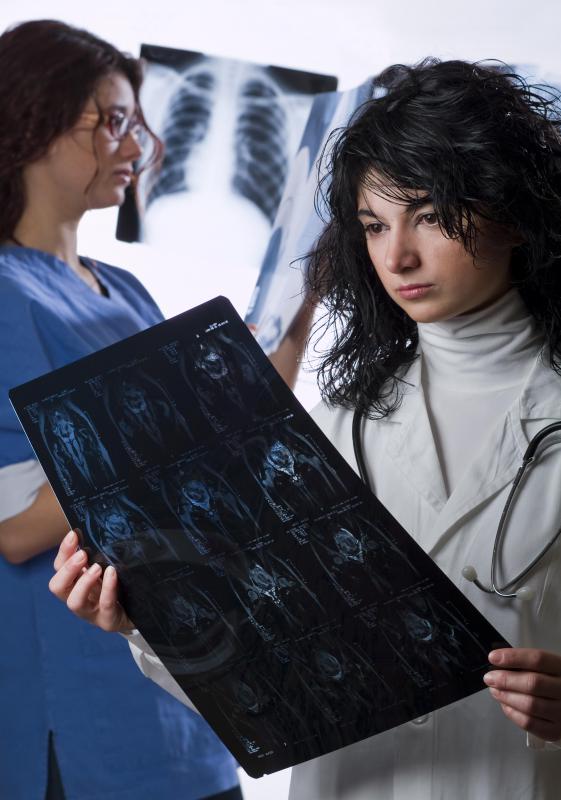
A bronchogenic cyst is a congenital cyst, typically found in the central area of the chest cavity. Many people live with bronchogenic cysts their entire lives and are unaware of it, while others may experience symptoms which lead to a diagnosis. More commonly, the cyst is an incidental finding on a medical imaging study performed for another purpose. If a doctor determines that treatment is necessary, a surgery can be performed to remove the cyst.
Bronchogenic cysts form during fetal development. They consist of little pockets lined with respiratory epithelium, which is characterized by the presence of small hair like structures called cilia. Sometimes the cyst will be filled with air or fluid, and some have mucus glands. Cysts can be found around the trachea, lungs, and upper area of the sternum. The walls of the cyst are usually thin and the structure can vary in size.

In infants and young children, sometimes a bronchogenic cyst puts pressure on vital organs and can potentially be dangerous because the patient may have difficulty breathing or experience other medical issues. In adults, bronchogenic cysts sometimes rupture, leading to infection, and they have also been linked with some cases of obstructive pneumonia. For most people, however, a bronchogenic cyst poses no threat and may never be detected.

Detection of bronchogenic cysts is rare, but it should not be assumed that the cysts themselves are rare. Determining incidence rates is very difficult because they are rarely diagnosed. Medical imaging studies of the chest are necessary to diagnose a bronchogenic cyst and sometimes the unusual growth is hard to see, especially if a radiologist has not seen very many during her or his career. When patients present with symptoms which might be indicative of a bronchogenic cyst, a doctor can request a medical imaging study to check. Sometimes prenatal ultrasound also reveals these structures.

If a doctor does identify a bronchogenic cyst, the options can be discussed with the patient. Surgery may be recommended because there are concerns about the risk of rupture or infection and it can be advisable to simply remove the cyst so that these risks are not an issue. However, if a patient is not a good candidate for surgery, the doctor may recommend a wait and see approach to see if the cyst can be managed without surgery. Patients may also find it helpful to obtain a second opinion from another practitioner.
AS FEATURED ON:
AS FEATURED ON:















Discussion Comments
I had a friend in school with a bronchogenic cyst. He didn’t know he had it until he started having a lot of trouble breathing one day. It sent him into a panic, and he hyperventilated.
The teacher called 911, and they put him on oxygen until they could get to the hospital to do an x-ray. The doctor found that he had a cyst right where his trachea branched off. The cyst was so large that it was compressing the trachea.
He had no other option but surgery. The doctor performed robotic resection, where a computer translated his hand movements to the robot, which removed the cyst.
My fifteen-year-old niece discovered that she had a bronchogenic cyst after she developed fever from an infection. She was having some trouble swallowing and breathing, so her doctor decided to do an esophagram.
She had to drink a liquid containing barium sulfate. Then, the doctor did several x-rays of her esophagus. He saw the bronchogenic cyst, and he recommended surgery to remove it.
My niece had video assisted thoracic surgery. It involves less recovery time and less pain than open chest surgery. She received anesthesia, and then her doctor made some small incisions in her chest. He put a thorascope in there, and the camera showed him where to cut as he viewed the monitor.
Post your comments