At AllThingsNature, we're committed to delivering accurate, trustworthy information. Our expert-authored content is rigorously fact-checked and sourced from credible authorities. Discover how we uphold the highest standards in providing you with reliable knowledge.
What is a Bacterium?
A bacterium is a unicellular microorganism which represents one of the most basic and primitive forms of life. Bacteria are everywhere, from pools of nuclear waste to deep inside the Earth's crust, and it is believed that bacteria were the first living organisms on Earth. You come into contact with bacteria constantly, although you may not be aware of it. Bacteria exist in such abundance that scientists have barely begun to scratch the surface of the bacterial life on Earth, although some species are well known to humans because they cause infections or disease.
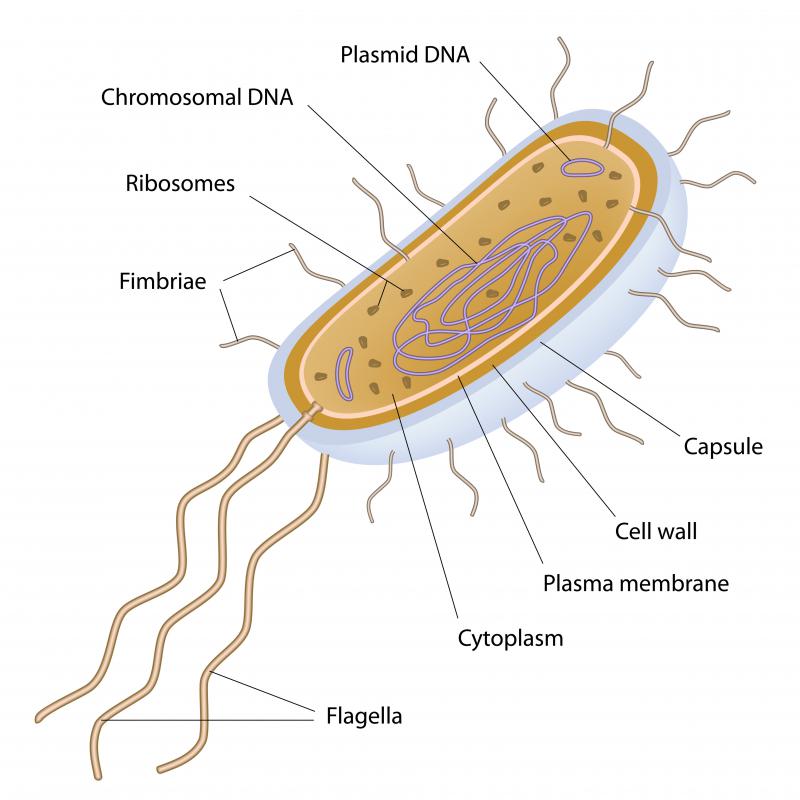
Several things are common to all bacteria, regardless as to how they live their lives. The organisms are classified in the kingdom Prokaryota, which used to be known as Monera. There are only two domains in this kingdom: bacteria and archaea. Bacteria lack a cell nucleus, and they also do not have organelles, like most other celled organisms do. Organelles are small structures inside a cell which have specific functions, like mitochondria. A bacterium has a single DNA molecule, along with RNA strands to help it replicate.

The study of bacteria is known as bacteriology. The more the organisms are studied, the more surprises they yield. A bacterium can come in a range of shapes, although most break down into rod, spiral, or curved shapes. The organisms typically use small hairs attached to their cell walls known as flagella to move around, and a bacterium may have one flagella or a plethora. In most cases, bacteria are surrounded by a hard outer shell which helps to protect them from the elements. This shell allows a bacterium to put itself into stasis, waiting for more congenial conditions to emerge.

A bacterium can live in a number of different ways. Some species are free living, meaning that they exist independently in things like soil, air, and water. Others may form relationships with additional bacteria or other organisms, taking advantage of mutual strengths to survive. In some cases, bacteria may colonize an animal, although they are perfectly capable of living without their host; bacteria use the host as a source of food, not necessarily for shelter. In most cases, bacteria actually assist their hosts, helping them to digest and break down food, and consuming cast off skin and hair. In other instances, as with pathogenic bacteria, the colonization results in an illness such as plague, tuberculosis, or cholera.

Many people are familiar with the rapid multiplication of bacteria, which can be accomplished in a number of ways. Most commonly, a bacterium grows and splits itself, thus creating exponential growth within a colony as each new generation grows and splits, sometimes within minutes. Bacteria can also exchange genetic information, including mutations, with each other. Some bacteria can also reproduce through budding, growing a portion of a parent cell which breaks off and grows into a new bacterium.
Frequently Asked Questions
What exactly is a bacterium?

A bacterium is a single-celled microorganism that belongs to the domain Bacteria. These microscopic entities are characterized by their simple cellular structure without a nucleus, which classifies them as prokaryotes. Bacteria can be found in virtually every environment on Earth, from soil and water to extreme habitats like hot springs and radioactive waste.
How do bacteria reproduce?

Bacteria primarily reproduce through a process called binary fission, which is a form of asexual reproduction. During binary fission, a single bacterium duplicates its genetic material and divides into two identical daughter cells. This process can occur rapidly, sometimes in as little as 20 minutes, leading to exponential population growth under optimal conditions.
Are all bacteria harmful to humans?
No, not all bacteria are harmful to humans. In fact, the human body hosts a vast number of beneficial bacteria, particularly in the gut, which are essential for digestion, vitamin production, and protecting against harmful pathogens. While some bacteria can cause diseases, many others play crucial roles in ecosystems, industry, and medicine.
What role do bacteria play in the environment?
Bacteria are pivotal in environmental processes such as nutrient cycling, decomposing organic matter, and fixing atmospheric nitrogen into forms usable by plants. They are also involved in bioremediation, which is the use of microbial metabolism to remove pollutants from the environment. Their diverse metabolic capabilities make them essential for maintaining life on Earth.
How can bacteria be used in biotechnology and medicine?
In biotechnology, bacteria are engineered to produce pharmaceuticals, like insulin, and enzymes for industrial processes. According to the American Chemical Society, genetically modified bacteria have been crucial in manufacturing drugs for diseases such as diabetes and growth disorders. In medicine, bacteria are used in developing antibiotics, vaccines, and are studied to understand disease mechanisms.
Can bacteria develop resistance to antibiotics?
Yes, bacteria can develop resistance to antibiotics through mutations and acquiring resistance genes from other bacteria. This process is accelerated by the overuse and misuse of antibiotics, leading to the emergence of 'superbugs' that are difficult to treat. The World Health Organization has declared antibiotic resistance as one of the biggest threats to global health, food security, and development today.
AS FEATURED ON:
AS FEATURED ON:














Discussion Comments
Not only are bacteria important in research and clinical medicine, but they are also vital to many beneficial activities that take place in the environment.
@anon14777: The most important class of bacteria takes into account the important aspect of bacteria reproduction and growth.
Autotrophs, (autotrophic bacteria), requires carbon and obtains it from carbon-dioxide. Some autotrophs use sunlight to produce sugar from carbon dioxide. Others depend on chemical reactions.
Heterotrophic bacteria obtain carbon dioxide from the environment (or living organism) that they are in.
@anon14777: Bacteria are classified based on their need of oxygen for their survival. The bacteria that must have oxygen are called aerobic bacteria. On the other hand, some bacteria cannot bear oxygen and could die if in an oxygenated environment. Those bacteria are called anaerobic.
what are the kinds of bacterium?
Post your comments