At SmartCapitalMind, we're committed to delivering accurate, trustworthy information. Our expert-authored content is rigorously fact-checked and sourced from credible authorities. Discover how we uphold the highest standards in providing you with reliable knowledge.
What Are the Steps in an Operational Audit?
There are typically six steps in an operational audit that range from preparatory work conducting interviews and collecting documents to the presentation of the final written report. An audit should be customized to meet a company's specific needs, so standard steps can only serve as a guideline. Management and its internal and external auditors will adjust the process to address the company's particular goals and objectives.
An operational audit is a review of the internal processes of a company. Its goals are to determine if company resources are being used efficiently and to identify ways to improve systems. The review includes various tasks, such as financial controls, the condition of equipment, and human resources allocations. Larger companies typically have an internal audit department that will handle the operational audit. Some companies will bring in outside consultants who specialize in operational reviews to do the audit or to work in conjunction with internal staff.

The first step in an operational audit is to structure the upcoming review. This could entail holding a meeting to outline expectations and to answer questions about the process. An external auditor will use this step to gather pertinent information about the company and set goals and objectives for the audit. This introductory step establishes the scope of the review.

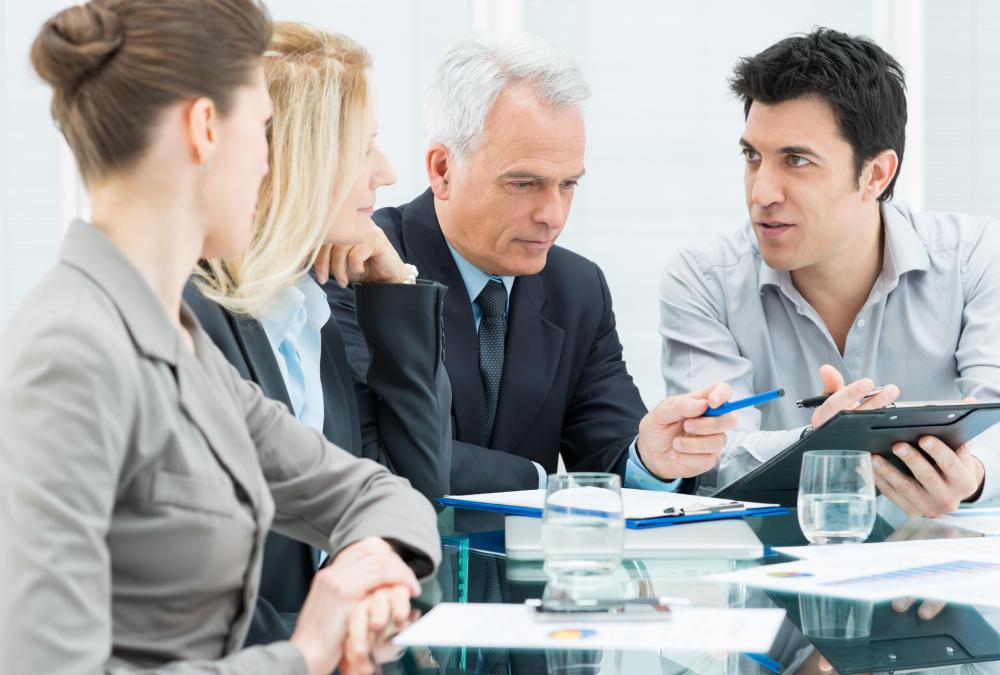
Steps two and three of the audit are the surveys of management and of the employees. Managers are typically interviewed for details concerning company systems and procedures. Employees are interviewed and observed in their work environments. Observation can lead to important insights into operational deficiencies that would not be evident through an interview.
The presentation of the audit plan is typically the fourth step in an operational audit. An audit plan is a written agenda that details the steps the company will have to follow to complete the audit. It is customized and based on the information the auditor gathered in the previous steps.
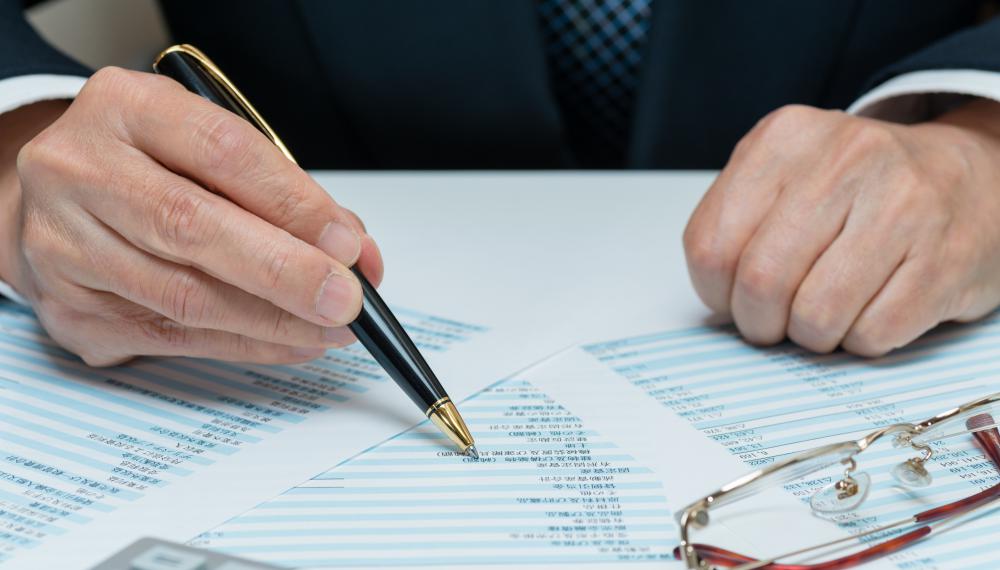
Step five is the actual audit. The auditor implements the audit plan, which ordinarily includes a review of the company's productivity and sales efforts. On the financial side, he assesses billing, cash flow management, and reporting processes. The company's risk management procedures are also ordinarily included in the audit. An operational audit can include these areas and any others that management thinks need a third party assessment.
In the sixth step, the auditor produces a final written report. It details his conclusions and recommendations. This report can be hundreds of pages long, depending upon the size of the company and the number of operational areas that were included in the audit.
AS FEATURED ON:
AS FEATURED ON:










Discuss this Article
Post your comments