At TheHealthBoard, we're committed to delivering accurate, trustworthy information. Our expert-authored content is rigorously fact-checked and sourced from credible authorities. Discover how we uphold the highest standards in providing you with reliable knowledge.
What Are the Functions of the Occipital Lobe?
The occipital lobe, which is part of the human brain, is primarily responsible for processing and relaying visual cues. This lobe makes up one section of the larger cerebral cortex. It receives information from the eyes and optical nerves, then directs those signals to either the primary visual cortex or either of two levels of visual association cortex. The result is what’s broadly known as visual processing data, basically information that the brain uses to interpret and make sense of things that are seen. In healthy people, this lobe functions flawlessly all on its own, but problems usually lead to profound vision issues. Defects with brain formation in this section can lead to blindness or profound sight impairment, for instance, and injuries impacting this area can also cause a range of sometimes irreversible visual impairments.
The Cerebral Cortex as a Whole

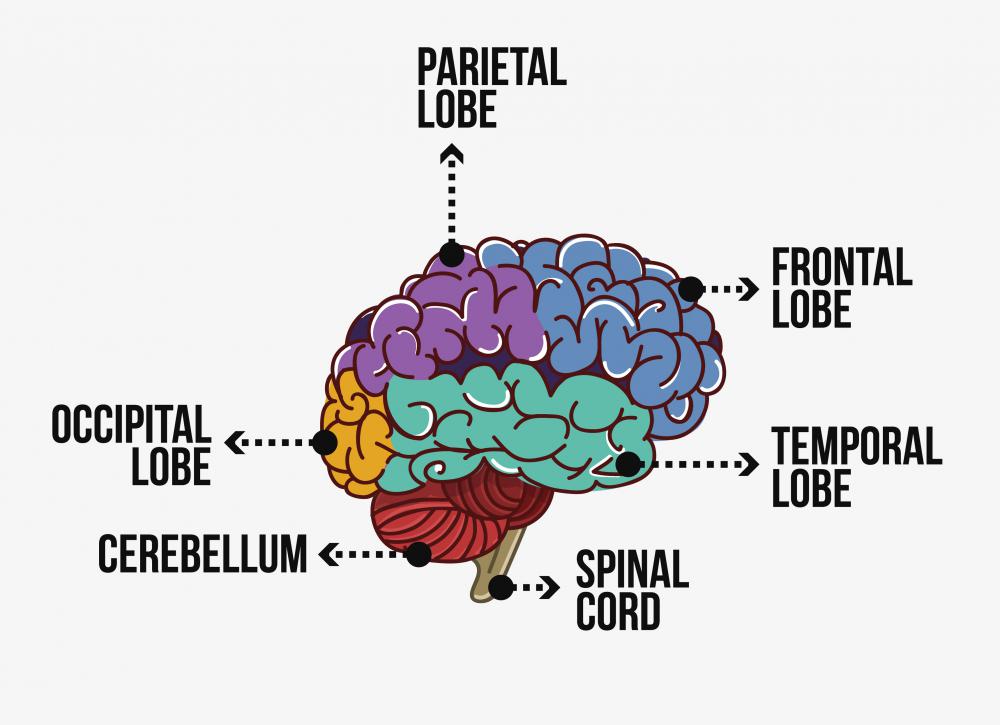
Although the brain often looks like one uniform spongy mass, it is made up of a number of complex interrelated parts. “Cerebral cortex” is the name given to the outermost layer, which in humans is the folded and ridged tissue layer most people can easily identify as brain mass. The cortex is made up of two hemispheres, but also four lobes. These are the frontal lobe, the temporal lobe, the parietal lobe, and the occipital lobe.

The frontal lobe is involved in movement and planning, while the temporal lobe is involved in auditory processing. The primary function of the parietal lobe is body perception, also known as “somatosensation,” while the occipital lobe, which is located towards the back of the cerebral cortex, is involved almost exclusively with vision.
Visual Processing

Visual processing happens through coordination with the optic nerves, which are connected to the eyes. These send information to the thalamus, another part of the brain, which then relays it on to the primary visual cortex. Typically, information that is received by the primary sensory cortex is sent directly on to the regions located adjacent to it, called the sensory association cortex.

One of the main functions of the occipital lobe is to send information from the primary visual cortex to the visual association cortex. The visual association cortex is located in more than one lobe, which means that the occipital lobe isn’t the only player when it comes to this important role. Together, these areas analyze the visual information received by the primary visual cortex and store visual memories.
Levels of Visual Association

There are two levels of the visual association cortex. The first level, located around the primary visual cortex, receives information about movement of objects and color. Additionally, it processes signals relating to the perception of shapes. The second level, located in the middle of the parietal lobe, is responsible for perception of movement and location. Things like depth perception are headquartered here. This level is also located in the lower part of the temporal lobe, which is responsible for processing and translating information about three-dimensional form.
Consequences of Damage
Damage to the functions of the occipital lobe can cause different visual impairments, most of which are somewhat serious. If the primary visual cortex is damaged completely, it will typically result in blindness. The primary visual cortex has a visual field mapped on its surface, and erasing or profoundly damaging this is usually irreversible. Complete damage is often a result of serious trauma, and can sometimes also happen as a result of a tumor or other irregular growth on the surface of the brain. Birth defects can also be to blame in rare instances.
Lesions to the visual association cortex are usually less dramatic. Blindness can still happen, but it’s not as likely; more commonly, patients have trouble recognizing objects, a deficit known medically as visual agnosia. For example, a patient may be able to pick up a clock and recognize the object through touch; however, if shown a picture of a clock, the patient will often only be able to describe elements of the picture, such as the round surface of a clock face or numerals placed in a circle.
Prognosis
Sometimes visual health can be restored through therapy or even surgery, but not always. A lot depends on the extent of the damage and what caused it, as well as the age of the patient. Younger people, particularly children, often respond to restorative therapy better than those who are older or whose brains have stopped growing.
AS FEATURED ON:
AS FEATURED ON:














Discussion Comments
@Slitherine - There is always hope here though. The brain is so difficult to work with, but we are cracking the code.
Brain matter can't be fixed, but with stem cells, in the future there may be a way to add new brain cells.
It is an exciting time in medical science. Stem cells may offer a whole brand new bridge to cure things once thought impossible.
Post your comments