At WiseGEEK, we're committed to delivering accurate, trustworthy information. Our expert-authored content is rigorously fact-checked and sourced from credible authorities. Discover how we uphold the highest standards in providing you with reliable knowledge.
What are the Different Types of Pituitary Tumor?
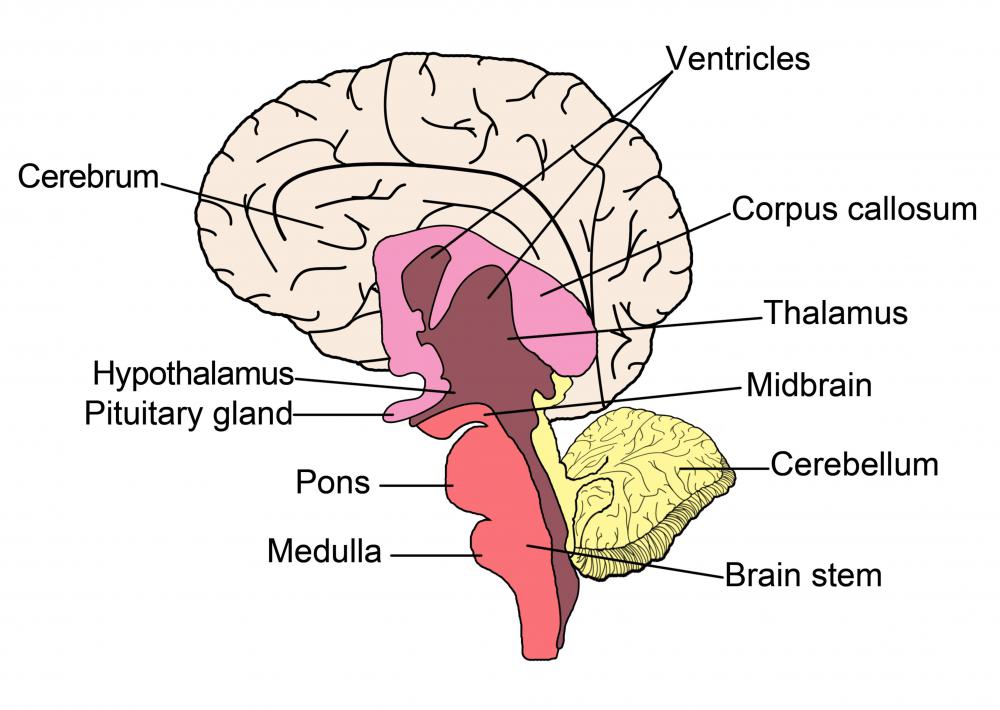
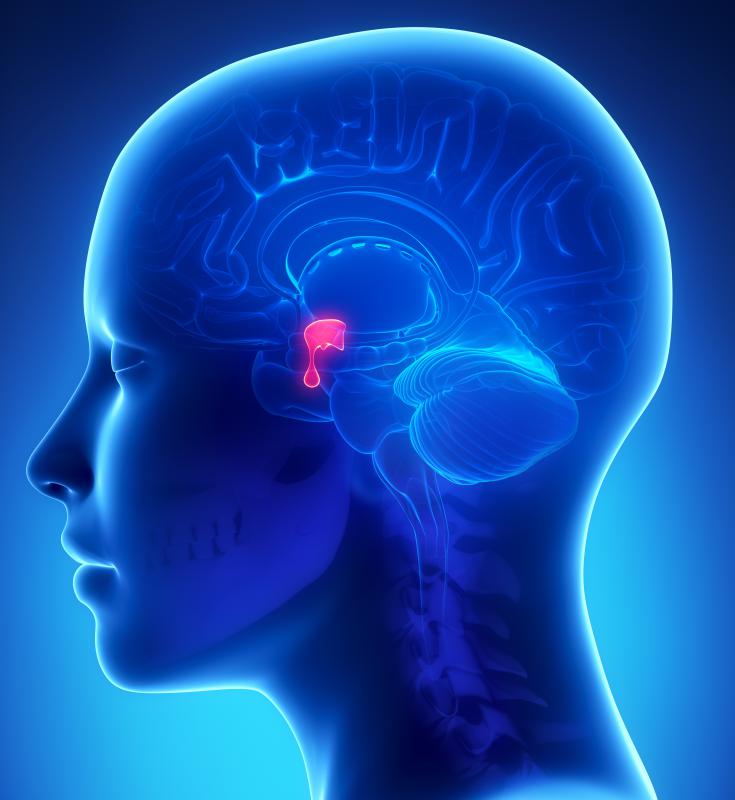
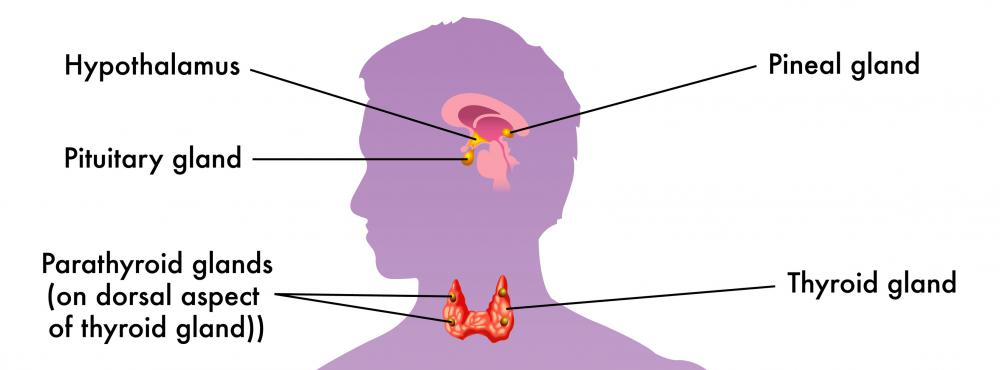
A pituitary tumor, or pituitary adenoma, is a solid mass of abnormally growing cells located in the pituitary gland, which is found at the lower part of the brain. Their sizes are usually in the smaller ranges, so pituitary tumors are difficult to detect and thus can continue to be undiagnosed until critical symptoms surface. The pituitary gland is technically not part of the brain and has a different composition from the brain tissues, so pituitary tumors are not considered to be brain tumors. The different types of pituitary tumors can be classified into various groupings, such as microadenomas or macroadenomas and functioning tumors or non-functioning tumors. They include adrenocorticotrophic tumors, gonadotrophic tumors, lactotrophic tumors, somatotrophic tumors and thyrotrophic tumors.
In terms of size, a pituitary tumor is called a microadenoma if it is smaller than 0.4 inches (10 mm) or a macroadenoma if it is larger than 0.4 inches (10 mm). A pituitary tumor is also classified as functioning if the tumor produces additional hormones or as non-functioning if it does not produce any hormones. Functioning pituitary tumors are further categorized, depending on the kind of hormones they secrete.

Adrenocorticotrophic tumors are those that produce adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH), which oversees the adrenal gland to produce regulated amounts of cortisol and adrenaline. Gonadotrophic tumors secrete luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), with help to stimulate menstruation in females and the production of sperm in males. Lactotrophic tumors, also known as prolactinomas, over-secrete prolactin, the hormone responsible for breast-milk production. Somatotrophic tumors produce excessive growth hormones, which can lead to the abnormal swelling of body parts such as the limbs, skull and hands. Thyrotrophic tumors secrete thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), which stimulates the thyroid gland to secrete hormones for metabolism and growth.

Functioning pituitary tumors produce excessive and unwarranted levels of hormones, so they can bring about certain diseases or irreversible conditions, such as gigantism, infertility, impotence and Cushing’s disease, among others. A pituitary tumor can be treated in several ways. The most common treatment is surgery to remove the pituitary tumor altogether. In some cases when tumors are found to be too small to be operated on, radiation treatments are an alternative treatment, or patients can wait until the tumor enlarges.

If radiation and surgical treatments cannot be done, medication can help reduce the tumor’s size or eliminate it or to regulate the hormone production of the pituitary gland. Persistent symptoms can indicate a presence of a pituitary tumor, such as headaches, nausea, blurred or loss of vision, increased or decreased appetite, early or late puberty and growth, irregular menstrual cycles and unexplainable mood swings. Consulting a physician is best when combined symptoms are experienced.
AS FEATURED ON:
AS FEATURED ON:















Discuss this Article
Post your comments