At WiseGEEK, we're committed to delivering accurate, trustworthy information. Our expert-authored content is rigorously fact-checked and sourced from credible authorities. Discover how we uphold the highest standards in providing you with reliable knowledge.
What Are the Different Parts of the Hypothalamus?
The hypothalamus has three parts: the anterior, tuberal, and posterior. Each part plays its own role in the overall functions and responsibilities of the endocrine system. General responsibilities include joining the endocrine system and nervous system. Most importantly, this small part of the brain maintains homeostasis, which is maintaining suitable conditions the body needs to function properly.
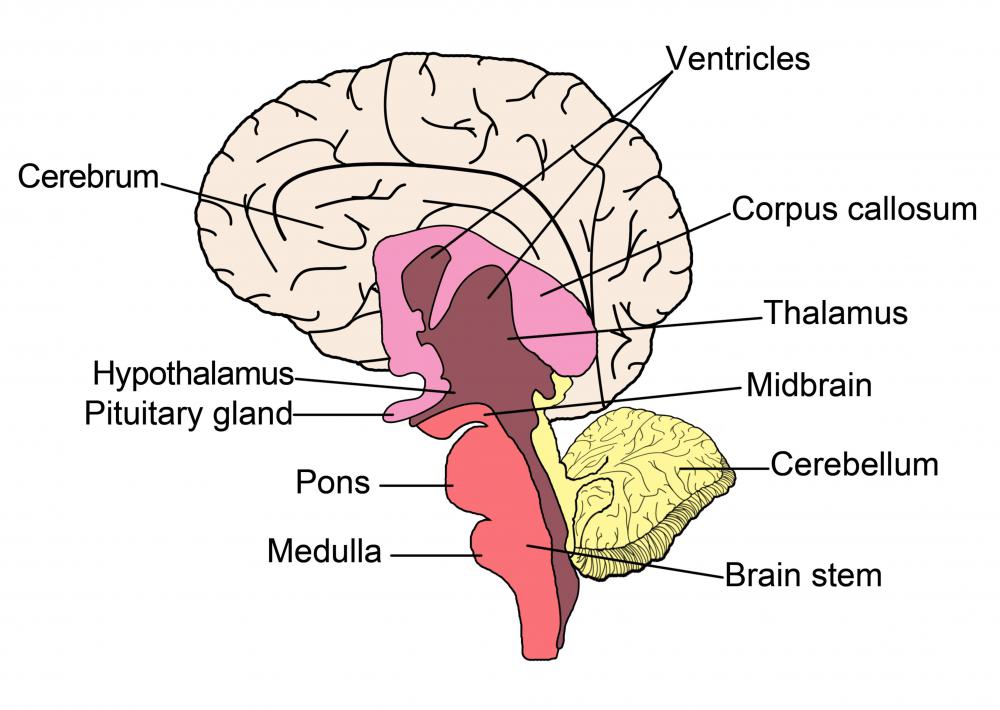
Although the hypothalamus is a small organ in the brain, it has large tasks to perform. It is shaped like a cone and is located above the brainstem, under the thalamus. This part stretches downward until it meets with the infundibular stalk, which is a tube that is joined to the pituitary gland. In general, this organ has multiple functions that are broken down into each of the three parts.

Due to how the hypothalamus is connected to multiple areas of the central nervous system and limbic forebrain, it must adjust according to different signals, both internal and external. Olfactory stimulation often affects endocrine hormones. Glucorticoids and steroids influence responses such as appetite or thirst. Exposure to daylight is an obvious signal; it helps regulate the sleep and wake cycle.

The anterior region of the hypothalamus is located in the front and is responsible for several functions. It is a crucial part of thermoregulation, which is the regulation of the body's temperature. Thermoregulation is controlled through sweating and panting. Sleep and circadian cycles are also regulated by the anterior region.
In the middle of the hypothalamus, the tuberal region is found. This part is in charge of thirst and hunger. The tuberal region also controls blood pressure and heart rate. Growth regulating hormones and dopamine production are regulated by this region as well.
On the back of the hypothalamus is the posterior region. Increases in blood pressure, shivering, and pupil dilation are controlled by this area. Memory functions are also influenced by this region.

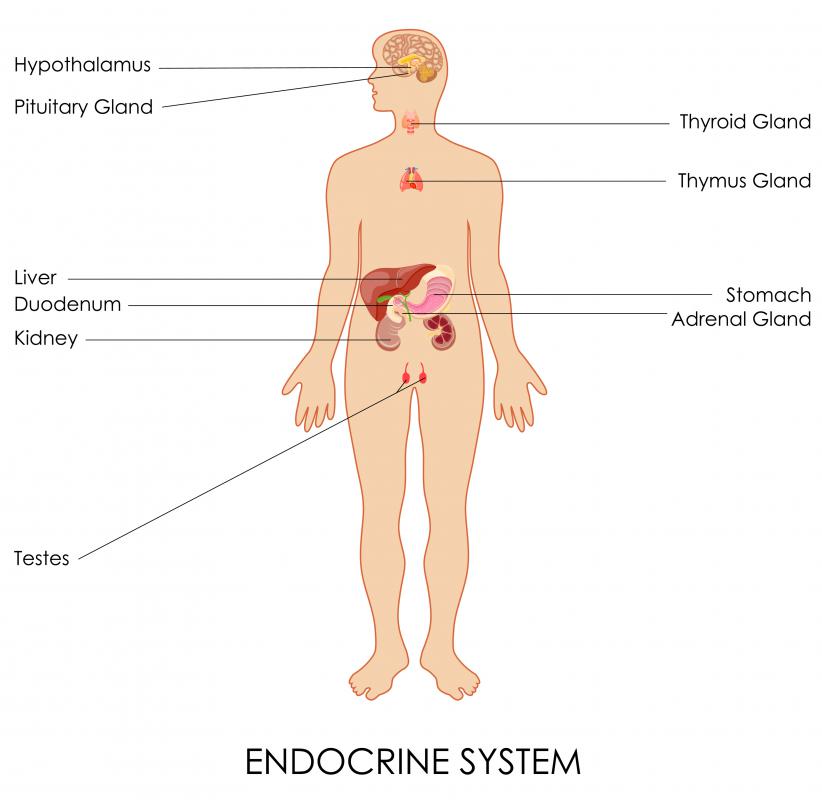
As a whole, the hypothalamus controls many important bodily functions. Neurohormones are controlled and released by this little organ in the brain. Through these hormones, pituitary gland activity is controlled, as well as the metabolic processes of the whole autonomic nervous system.
In addition to the hormones and control of the metabolic aspects, the hypothalamus also controls and releases hormones that influence the endocrine system. Endocrine hormones are sent to the pituitary gland and play a role in certain behaviors that are based on emotions, such as anger, anxiety or fear, and sexual activities.
AS FEATURED ON:
AS FEATURED ON:













Discuss this Article
Post your comments