At WiseGEEK, we're committed to delivering accurate, trustworthy information. Our expert-authored content is rigorously fact-checked and sourced from credible authorities. Discover how we uphold the highest standards in providing you with reliable knowledge.
What are the Different Microbiology Careers?
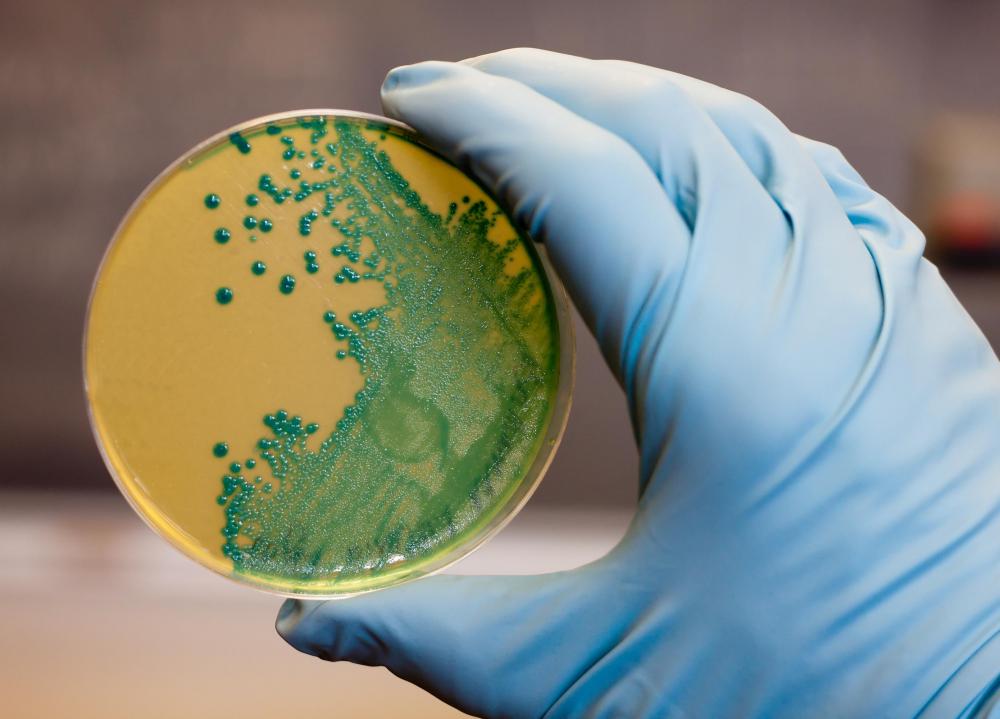
Microbiology is the scientific study of microorganisms such as bacteria, fungi, and other microbes. Since it is such a broad science, there are several different types of microbiology careers. Scientists frequently specialize in the type of organisms they study and the industries in which they work. Microbiology careers are available in a number of different settings, such as universities, pharmaceutical companies, biotechnology laboratories, and medical research hospitals.
Many microbiologists research specific types of microbes. A bacteriologist, for example, studies different types of bacteria to learn about their life cycles, structures, and functions. They may experiment with different types of antimicrobial solutions to eradicate harmful bacteria from samples. Virologists research the nature of viruses and how different strains develop. Mycologists focus on fungi, and protozoologists study algae and other protists.

Microbiology careers in all areas of specialization are found in several different work environments. Many microbiologists are employed by universities, where they may lead research teams in laboratories and teach advanced science courses. University microbiologists train new generations of researchers, supplying the tools and techniques they will use in their future microbiology careers.

Several microbiology careers are available in research and development institutions. Microbiologists employed by pharmaceutical companies typically work in teams develop affective medicines against various diseases. They may spend months or even years researching a specific virus or disease and the treatments which have been prescribed in the past. A team experiments with cultures and tissue samples to determine the effectiveness of new medications in fighting the malady. Once a medicine shows promise, microbiologists may suggest a clinical trial on animals or humans in order to confirm laboratory results.

The biotechnology industry employs microbiologists to determine how microscopic organisms can be helpful to society. Some microbiologists work in food science labs, studying preservatives, potentially helpful probiotics, and harmful pathogens found in food. Medical microbiologists might work in hospitals or medical laboratories, studying and diagnosing various bacterial and viral diseases. They are often trained physicians who actively engage in the treatment of such microbial diseases. Medical microbiologists are essential to advancement of microbial immunology, the study of the body's immune system and microorganisms which help and harm it.

Other microbiologists might engage in environmental science studies, researching soil, air, water, and living samples to determine how certain microbes thrive under different circumstances. Cellular microbiologists study the function and composition of microbes at their most basic level, and apply their findings to agricultural, food, and medical studies. Regardless of the discipline or industry, microbiologists are essential to keeping people healthy and unraveling the mysteries of a tiny world.
AS FEATURED ON:
AS FEATURED ON:















Discussion Comments
@jmc88 - You're right. I think people get too hung up on the first thing they think of when they hear about a field like microbiology rather than thinking about all of the other branches.
Before reading this article, I didn't realize there were so many microbiology jobs that weren't in the health field. It makes sense, but I wouldn't have thought about needing people to study how plants work. If we didn't know how plants use fertilizers and fight diseases, we would be a lot worse off. I'm sure microbiologists have also been involved with the foodborne illnesses that have popped up the last several years.
It doesn't sound like studying the soil would be all that exciting, but I know that there are tons of bacteria and insects living there that are especially important for plants.
@TreeMan - I would also remind you that whatever major you pick in college doesn't lock you in forever. If you start out in microbiology and decide you hate working in a lab, you can always find a related major like botany or wildlife conservation. That's what I did.
What I think a lot of people don't understand about microbiology is that it doesn't have to deal with "playing God." When I started my major, the stem cell research debate was popular in the news. A lot of people when they heard I was studying microbiology immediately thought I was going to try to clone humans.
Just like the article describes, there are thousands of jobs that are in no way related to cloning. If it weren't for microbiologists studying how our bodies work, we wouldn't have a quarter of the medical advances we have today.
@TreeMan - It is good you are thinking about what you want to do already. I started off studying molecular and cellular biology in college, so I can probably give you some advice about things to consider.
First off, biology classes will be important like you said. Chemistry will also be a major part of any microbiology curriculum. If you don't like chemistry, I would definitely start looking for a different career. There are plenty of other majors for people who like biology.
Like the article says, there are several microbiology career options. Whether you can get a job immediately will depend on your specialization and how willing you are to work in different situations. Overall, though, microbiology is a large field and should have plenty of jobs.
I have always thought things like this were interesting. I am a sophomore in high school right now and am thinking something like microbiology might be what I am interested in studying in college. I did well in my biology class last year and liked learning about how the cells and other parts of the body work.
What classes would be best for me to take if I decided this was something I wanted to do? Obviously, biology class will be important, but is there anything else that would help me?
Once you graduate, how hard is it to find careers in microbiology? The article talks about a bunch of different jobs, but are they readily available? Is there anything else I should think about?
Post your comments