At AllThingsNature, we're committed to delivering accurate, trustworthy information. Our expert-authored content is rigorously fact-checked and sourced from credible authorities. Discover how we uphold the highest standards in providing you with reliable knowledge.
Do Most Countries in the World Have Some Sort of Air Quality Standards?
Despite its increasing visibility as a global crisis, air quality standards are not currently monitored or regulated by many countries around the world. In particular, developing nations tend to shy away from air quality standards as the short-term benefits of industrial strength and increased national wealth outweigh the long-term benefits to limiting air pollution.
Clean air is a basic requirement for the healthy living of all humans and animals. Unfortunately, many of the fuel sources and another chemicals that humans use to make life simpler and more comfortable are creating a global threat. According to a World Health Organization (WHO) study on diseases caused by air pollution, the burning of solid fuels both outdoors and indoors contribute to more than two million premature deaths each year. More than half of these occur in developing countries, the so-called "Third World."

A 2006 call-to-action by the WHO notes that studies show a reduction of PM10 levels could reduce deaths in polluted cities by up to 15% annually. PM10 is a pollutant mainly released through the burning of fossil and other types of fuels. The WHO's proposed air quality guidelines are actually much more stringent than the national standards in many countries. Meeting the organization's recommended levels of PM10 and other pollutants could require a country to reduce its current levels by up to three times — a challenge to say the least.

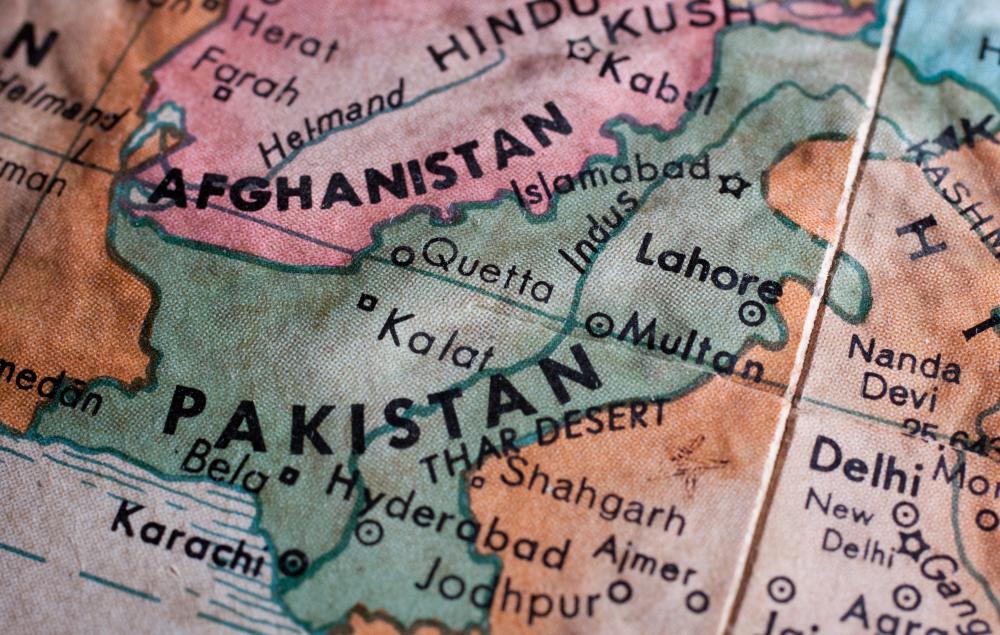
The national standards that do currently exist vary widely. Asia and the Middle East in particular suffer from a lack of appropriate air quality standards. China utilizes mass quantities of coal, a major source of PM10, as does India. Both of these countries have large populations simultaneously prospering and suffering from the use of fuels that compromise clean air. Worse, air pollution affects neighboring countries as air, obviously, cannot be restricted by borders. Some countries like Thailand and Malaysia are still following air quality standards from the 1980s, and as of 2006 there were no air quality standards set at all in Afghanistan, Bhutan, Lao or Pakistan.

Many critics have pointed out that industrial giants and world leaders like the U.S. and Great Britain have the technology and wealth to weather necessary and dramatic changes in air quality standards, but do not do nearly as much as they could to promote clean air efforts.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are air quality standards?
Air quality standards are regulations set by governments or international bodies to control the concentration of pollutants in the air. These standards are designed to protect public health and the environment by setting limits on pollutants like particulate matter, sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, and ozone. They are based on scientific research that indicates the levels at which air quality begins to pose a risk to humans and ecosystems.
Do most countries have air quality standards?

Yes, the majority of countries have implemented some form of air quality standards. According to the World Health Organization, over 80% of countries have air quality regulations or guidelines in place. These standards vary widely in their stringency and enforcement, reflecting the differing priorities and capabilities of nations around the globe.
How do countries enforce air quality standards?
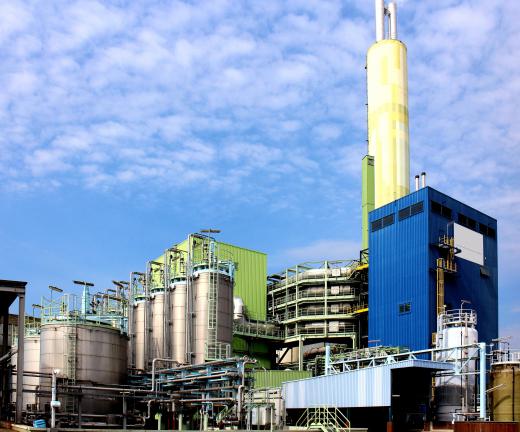

Countries enforce air quality standards through a combination of monitoring, regulation, and penalties. They establish networks of air quality monitoring stations to track pollutant levels. When standards are exceeded, governments may impose restrictions on industrial activities, vehicle use, and other sources of pollution. Non-compliance can result in fines, legal action, or mandatory measures to reduce emissions.
What is the role of the World Health Organization in air quality?
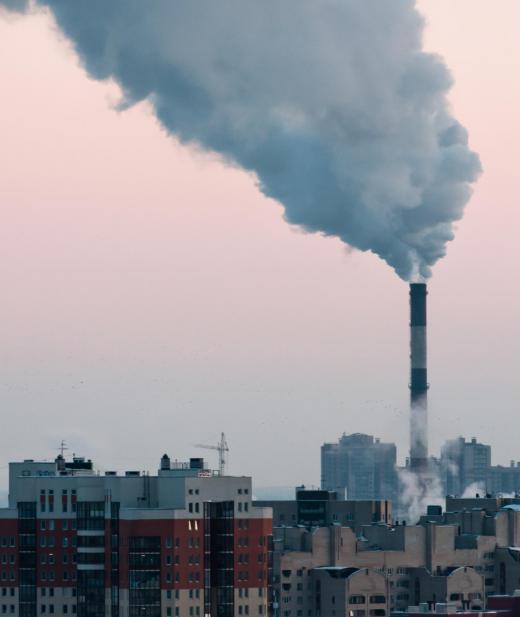

The World Health Organization (WHO) plays a crucial role in global air quality by providing guidelines and recommendations. The WHO's air quality guidelines offer a science-based benchmark for the safe levels of key air pollutants. While not legally binding, these guidelines influence national standards and are considered the gold standard for protecting public health from the dangers of air pollution.
Are there international agreements on air quality?
There are international agreements aimed at improving air quality, such as the Convention on Long-range Transboundary Air Pollution in Europe. These agreements facilitate cooperation between countries to reduce air pollution through shared standards, policies, and technology exchange. They recognize that air pollution does not respect borders and that collaborative efforts are essential for effective mitigation.
How do air quality standards differ between developed and developing countries?
Air quality standards often differ significantly between developed and developing countries. Developed nations typically have more stringent and comprehensive standards, along with the resources to enforce them effectively. In contrast, developing countries may have less strict standards and face challenges in enforcement due to limited financial and technical resources, as well as other pressing economic and social priorities.
AS FEATURED ON:
AS FEATURED ON:














Discussion Comments
According to Environmental Protection Agency, the amount of gas emissions from cars in United States, has dropped by 54 percent, while at that same time the number of cars has more than doubled. These figures reflect the numbers for the last 30 years, since 1970's.
This same, positive environmental trend seem to be working in Europe also.
Post your comments